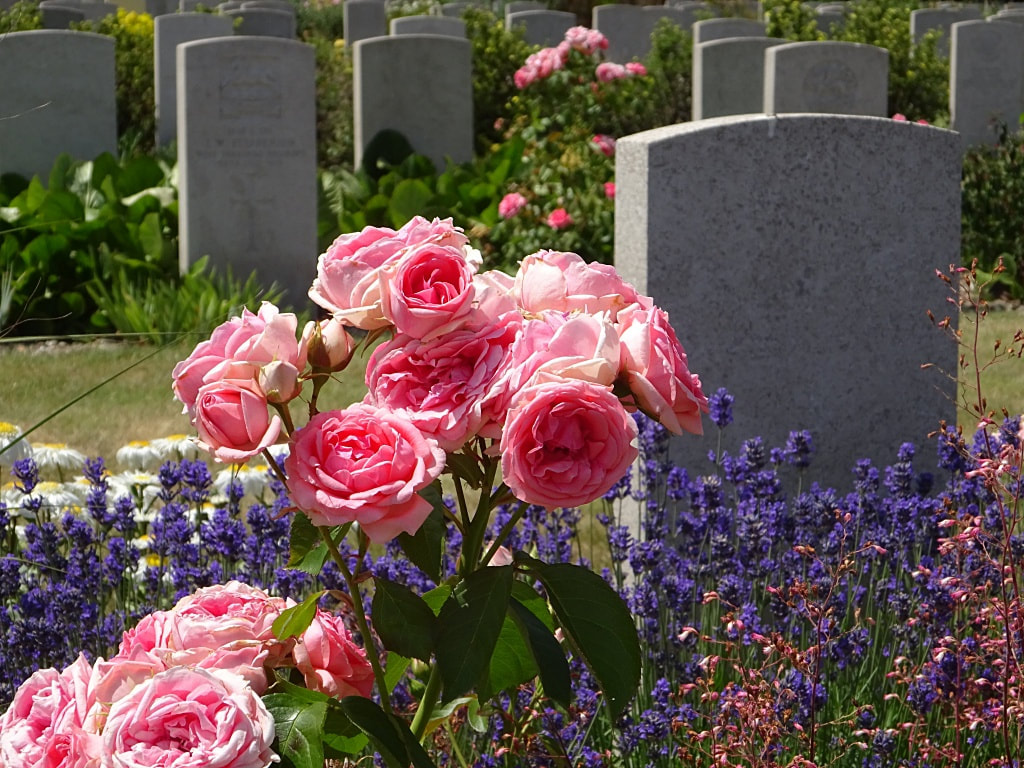
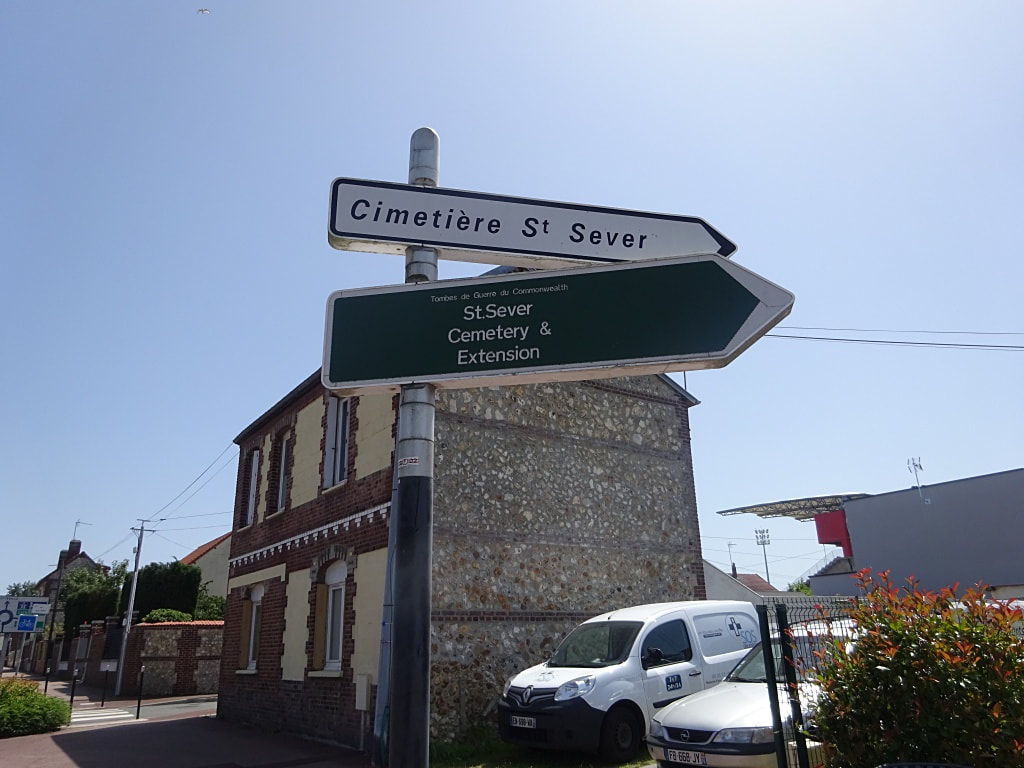
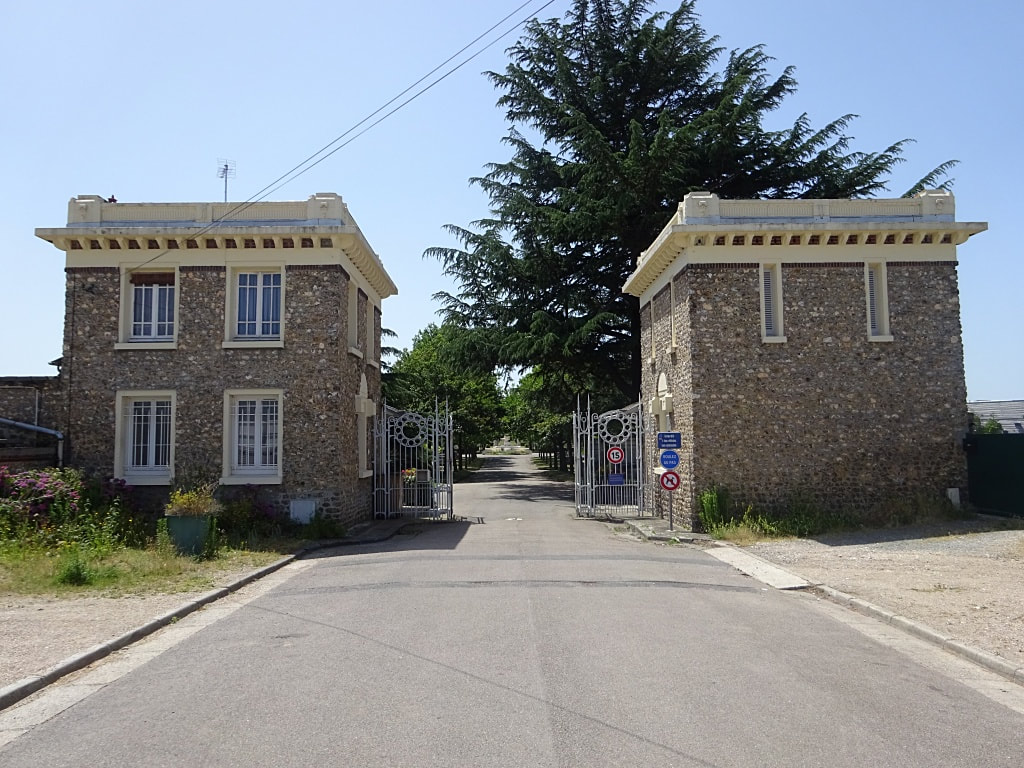
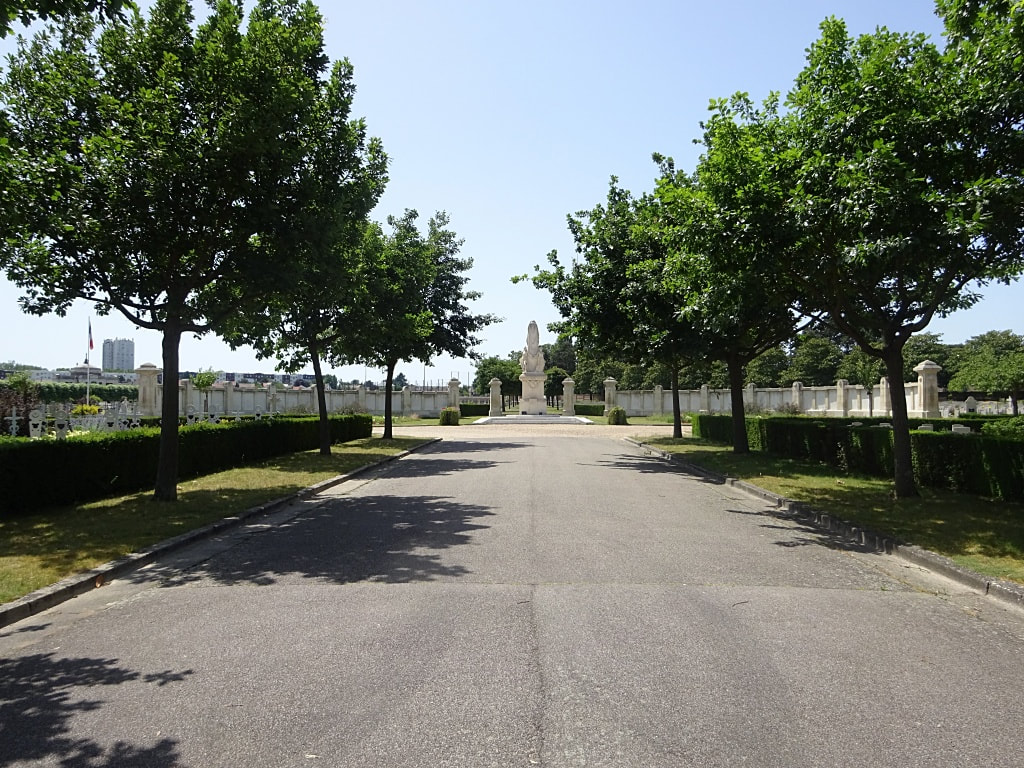
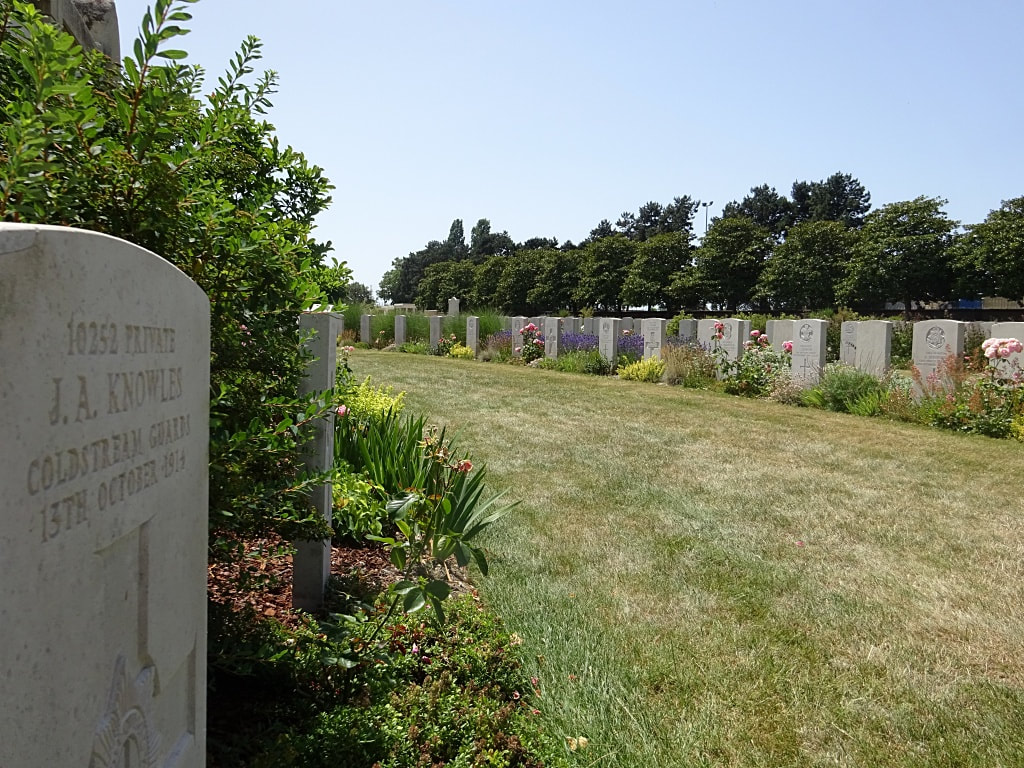
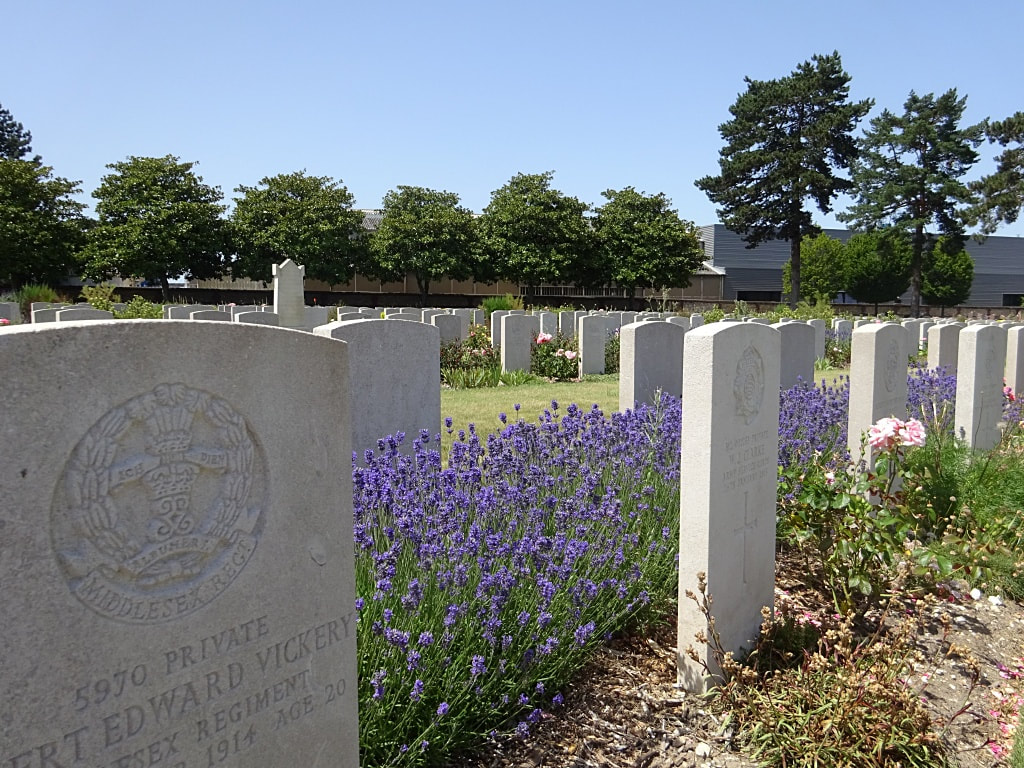
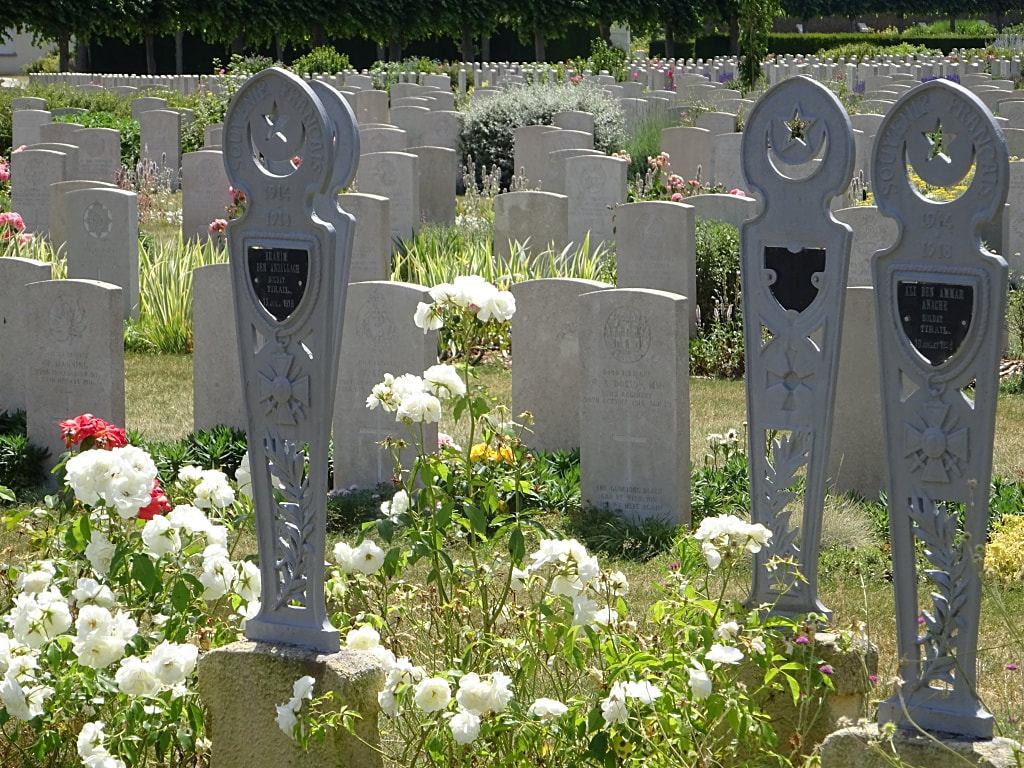
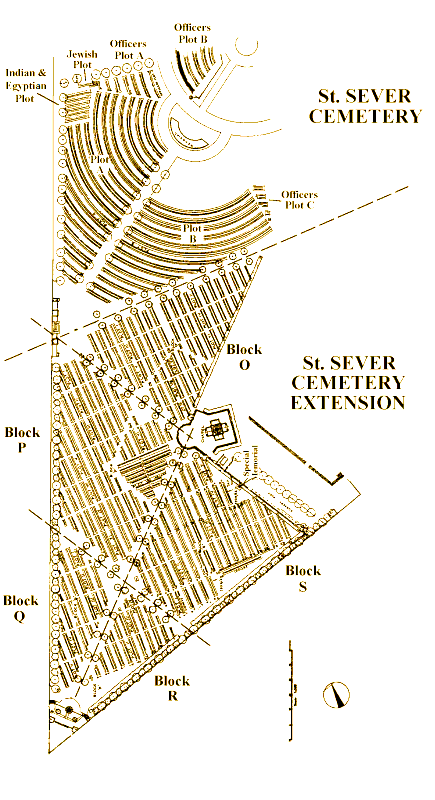
ST. SEVER CEMETERY
Rouen
Seine-Maritime
France
GPS Coordinates: Latitude: 49.41035, Longitude: 1.06698
Roll of Honour
Listed by Surname
Location Information
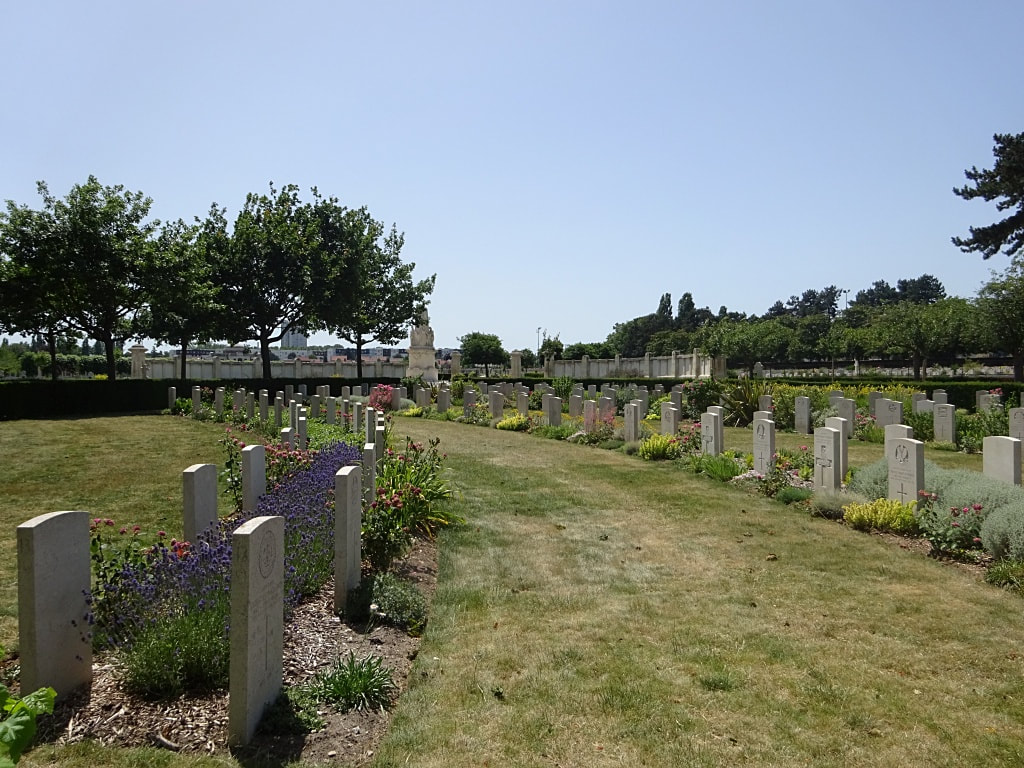
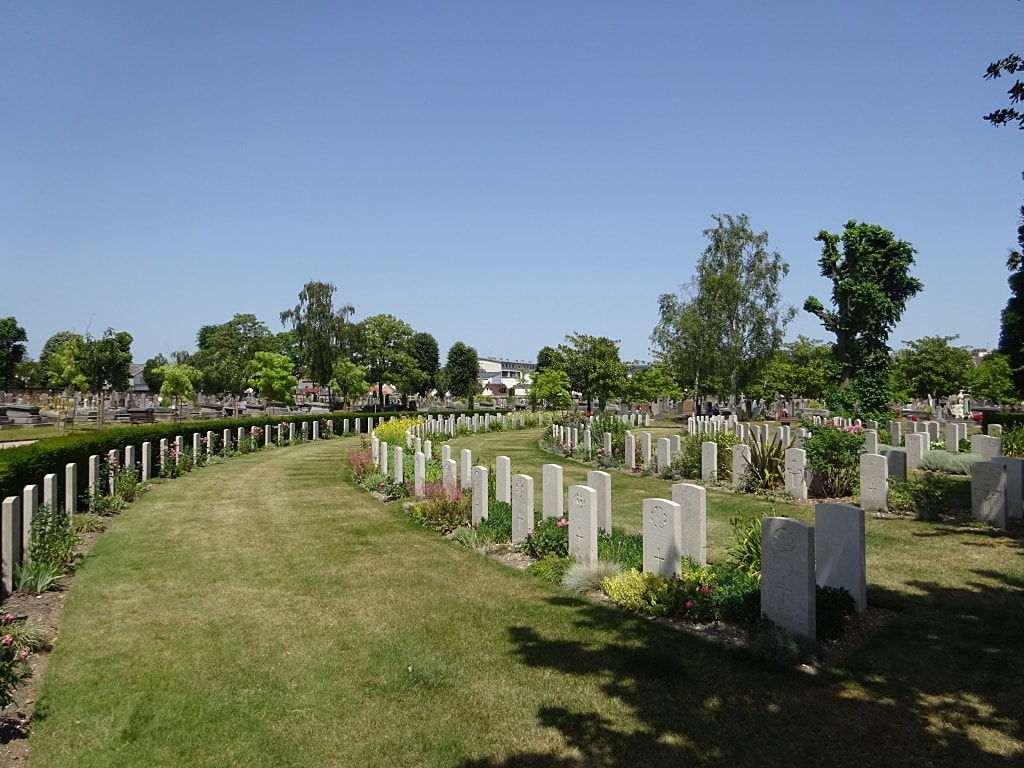
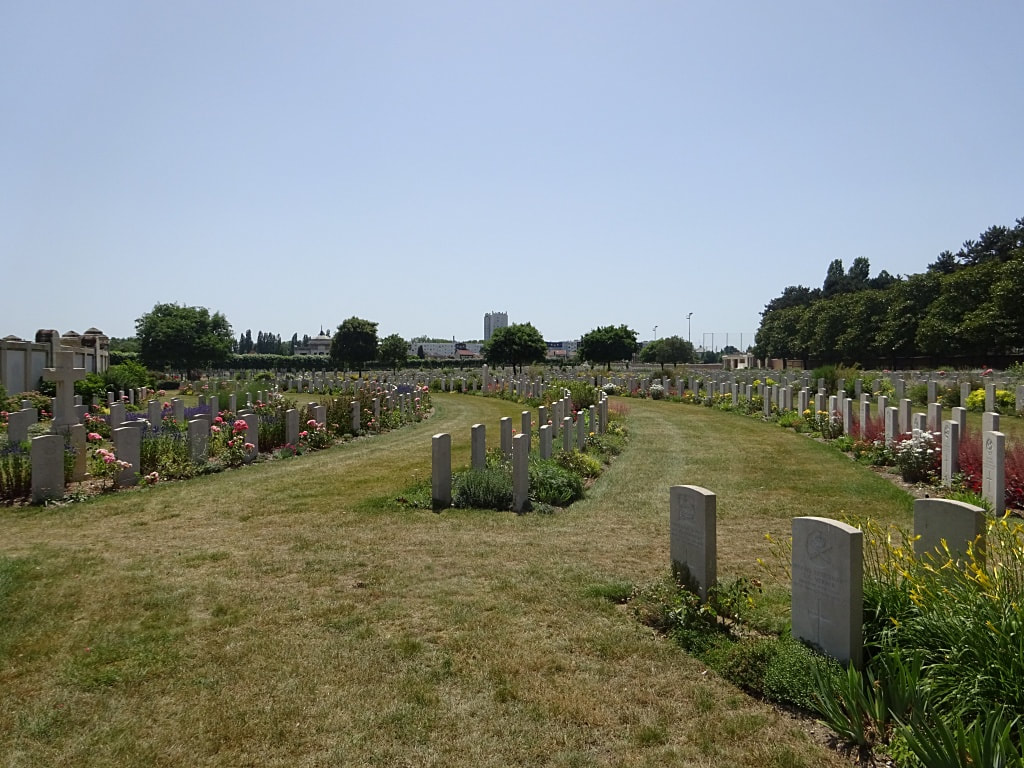
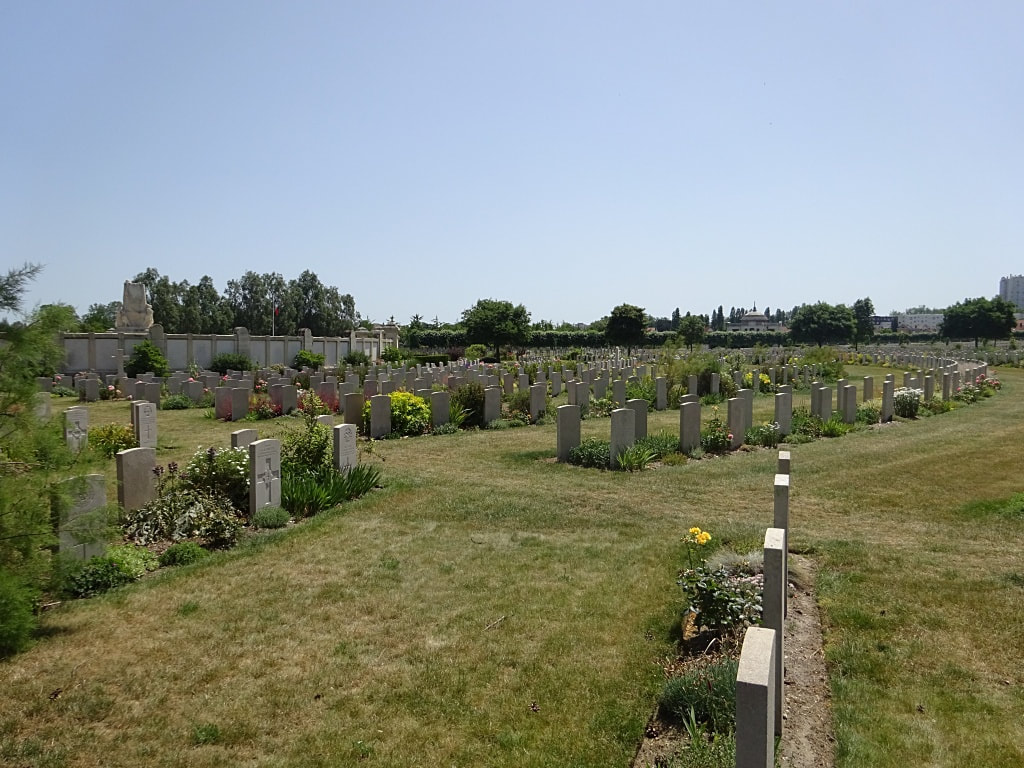
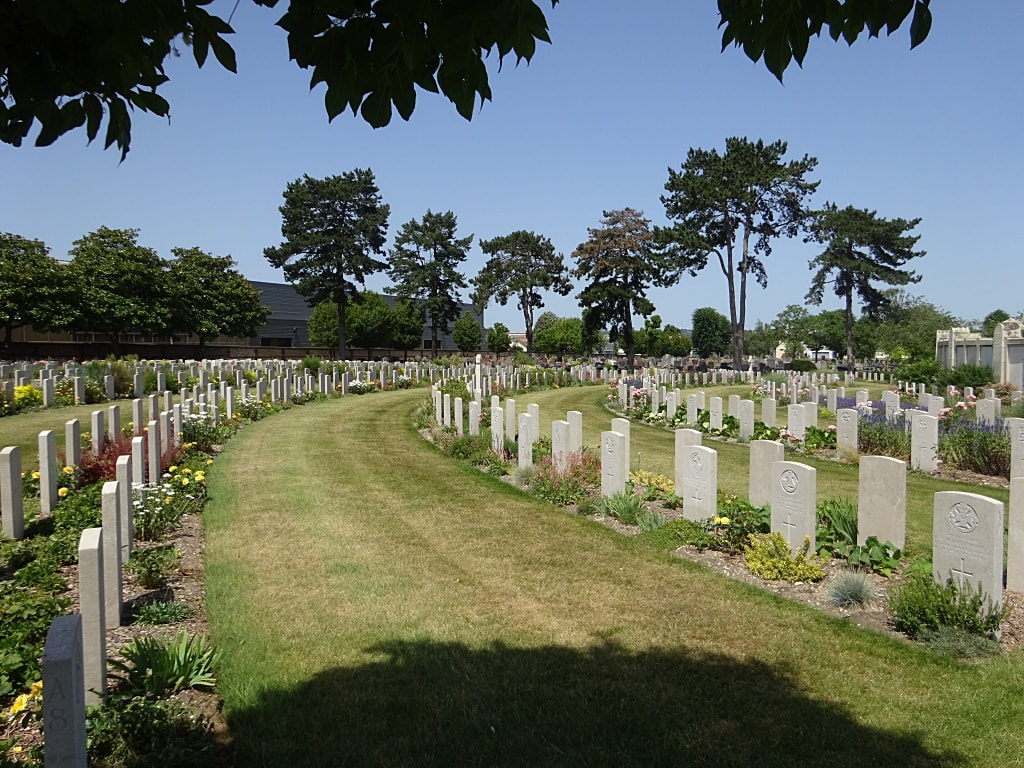
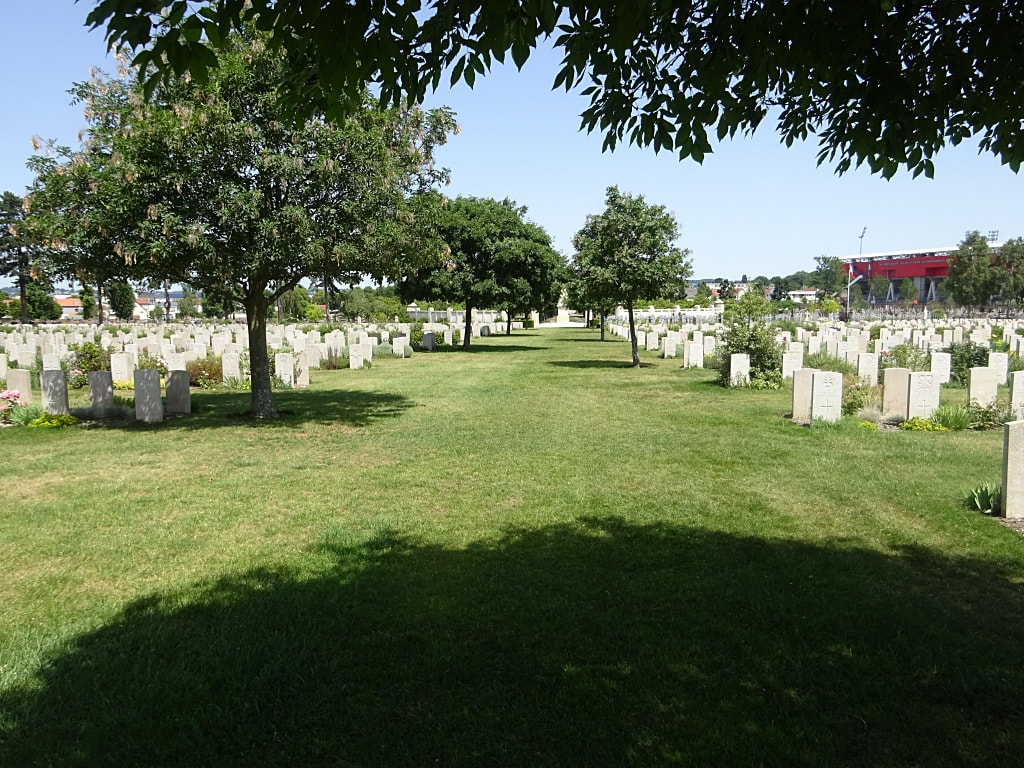
St Sever Cemetery and St Sever Cemetery Extension are located within a large communal cemetery situated on the eastern edge of the southern Rouen suburbs of Le Grand Quevilly and Le Petit Quevilly.
If approaching Rouen from the north, head for the centre of town and cross over the river Seine, following signs for Caen. Follow this route until you get to the 'Rond Point des Bruyeres' roundabout (next to the football stadium), then take the first exit into the Boulevard Stanislas Girardin. The cemetery is 150 metres down this road on the left.
If approaching Rouen from the south, follow the D938 (Avenue des Canadiens) towards the centre of town. At the 'Rond Point des Bruyeres' roundabout (next to the football stadium), take the fourth exit into the Boulevard Stanislas Girardin. The cemetery is 150 metres down this road on the left.
If arriving on foot, the easiest option is to take the Metro to the stop Charles De Gaulle in the Petit-Quevilly area and then walk east along the Boulevard Stanislas Girandin.
Visiting Information
OPENING TIMES
1 March - 1 November:
Monday-Saturday: 0815 - 1745
Sundays/Public Holidays : 0815 - 1745
2 November-28 February:
Every Day: 0815 - 1645
Historical Information
During the First World War, Commonwealth camps and hospitals were stationed on the southern outskirts of Rouen. A base supply depot and the 3rd Echelon of General Headquarters were also established in the city.
Almost all of the hospitals at Rouen remained there for practically the whole of the war. They included eight general, five stationary, one British Red Cross, one labour hospital, and No. 2 Convalescent Depot. A number of the dead from these hospitals were buried in other cemeteries, but the great majority were taken to the city cemetery of St. Sever. In September 1916, it was found necessary to begin an extension.
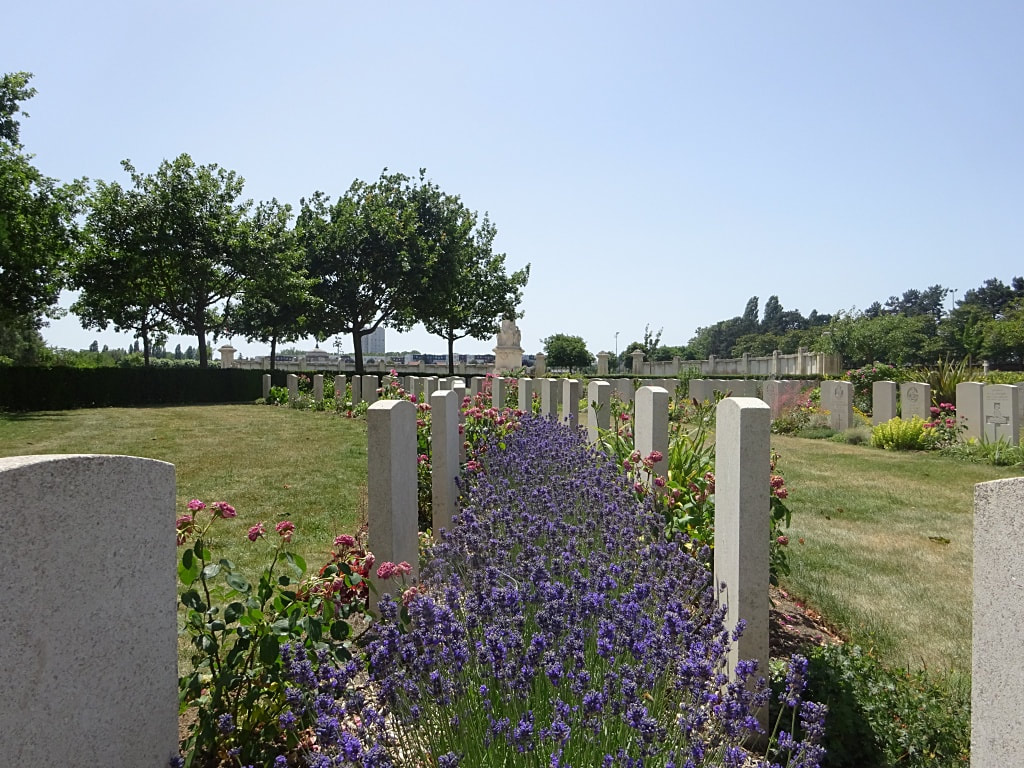
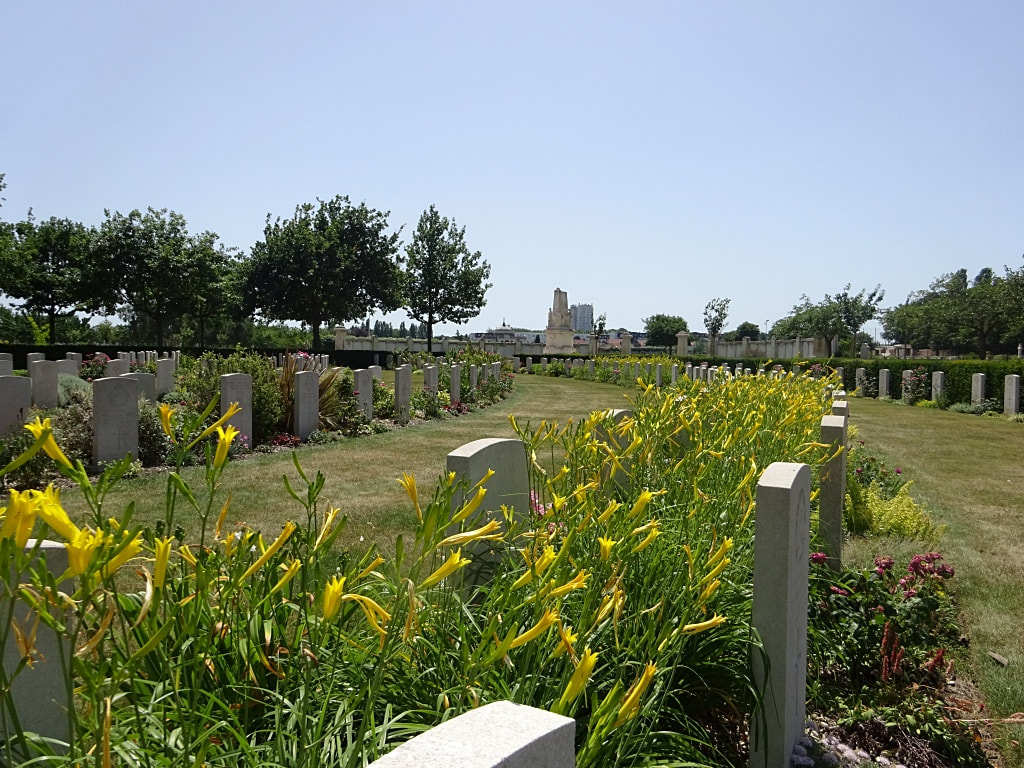
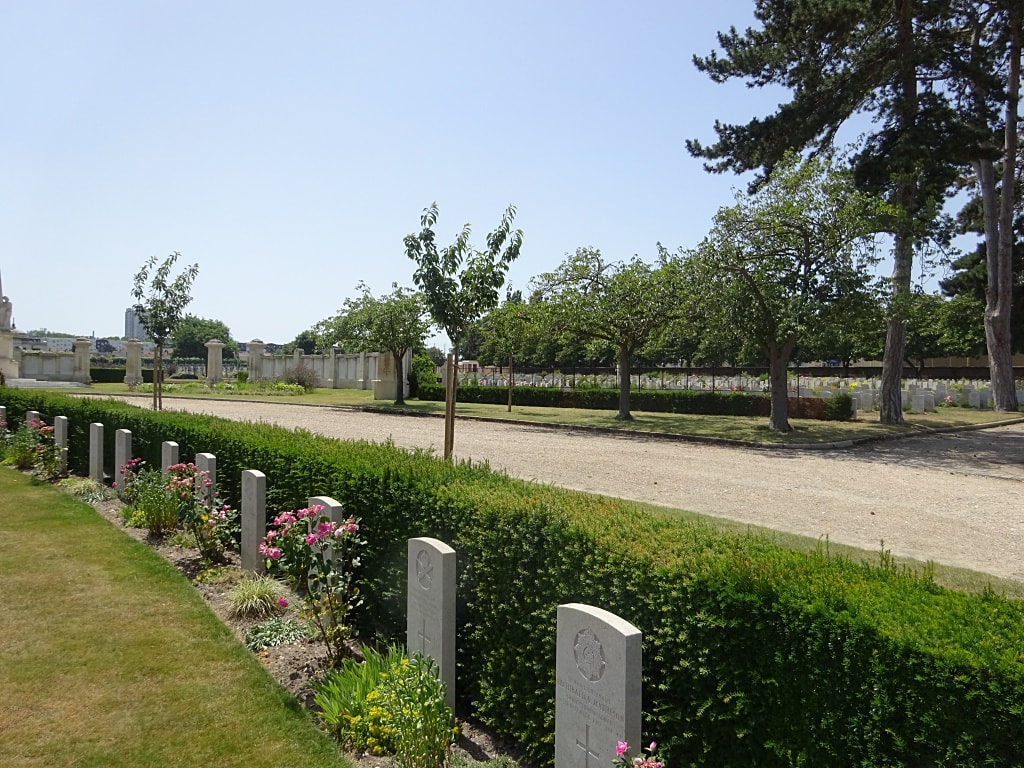
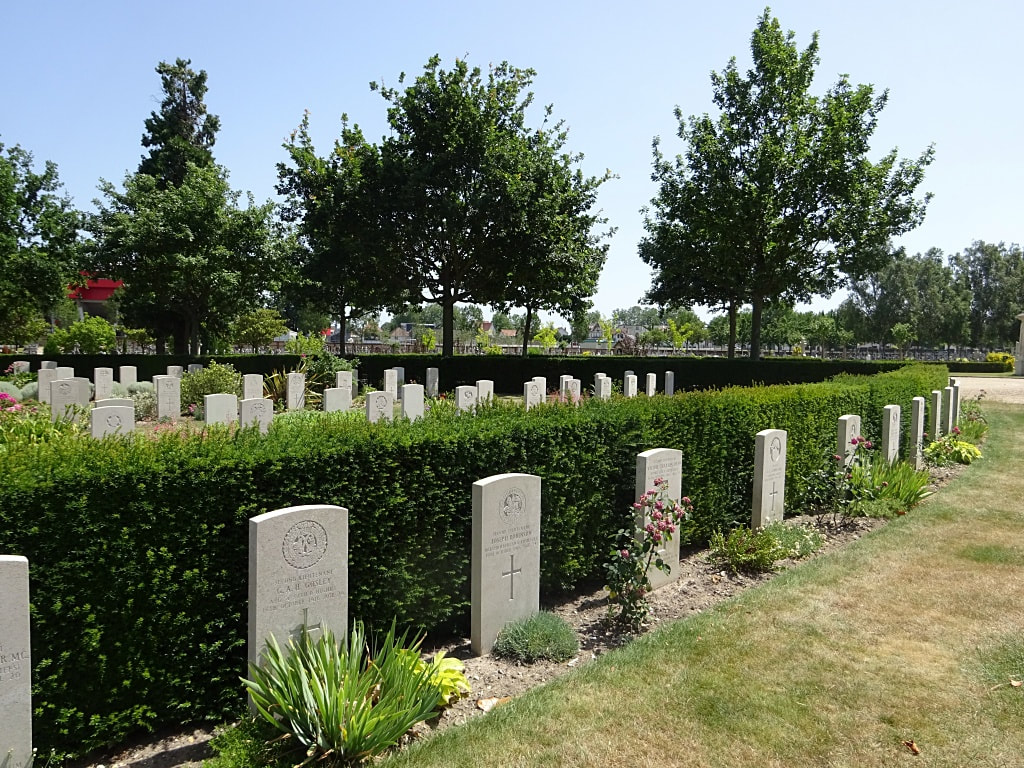
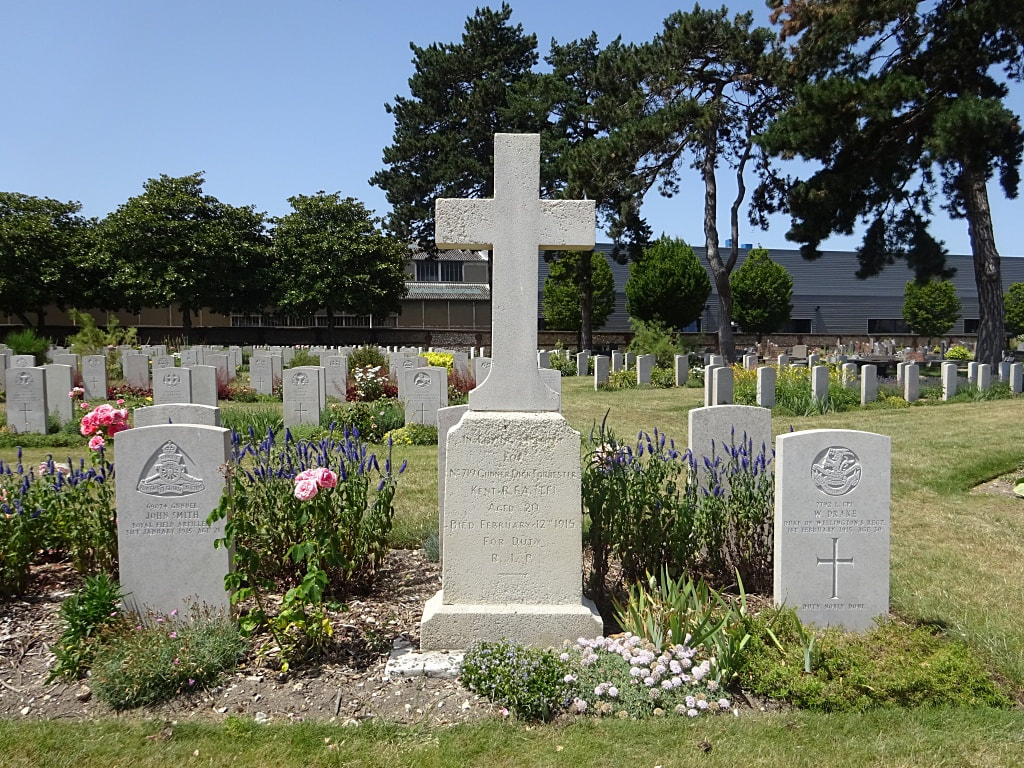
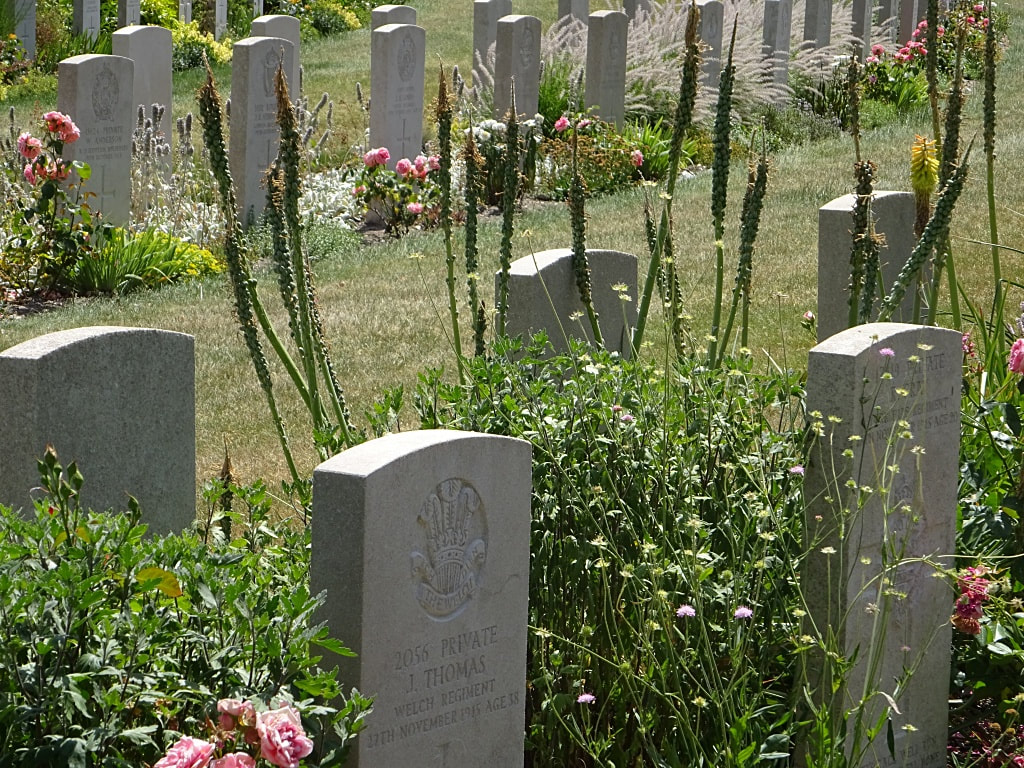
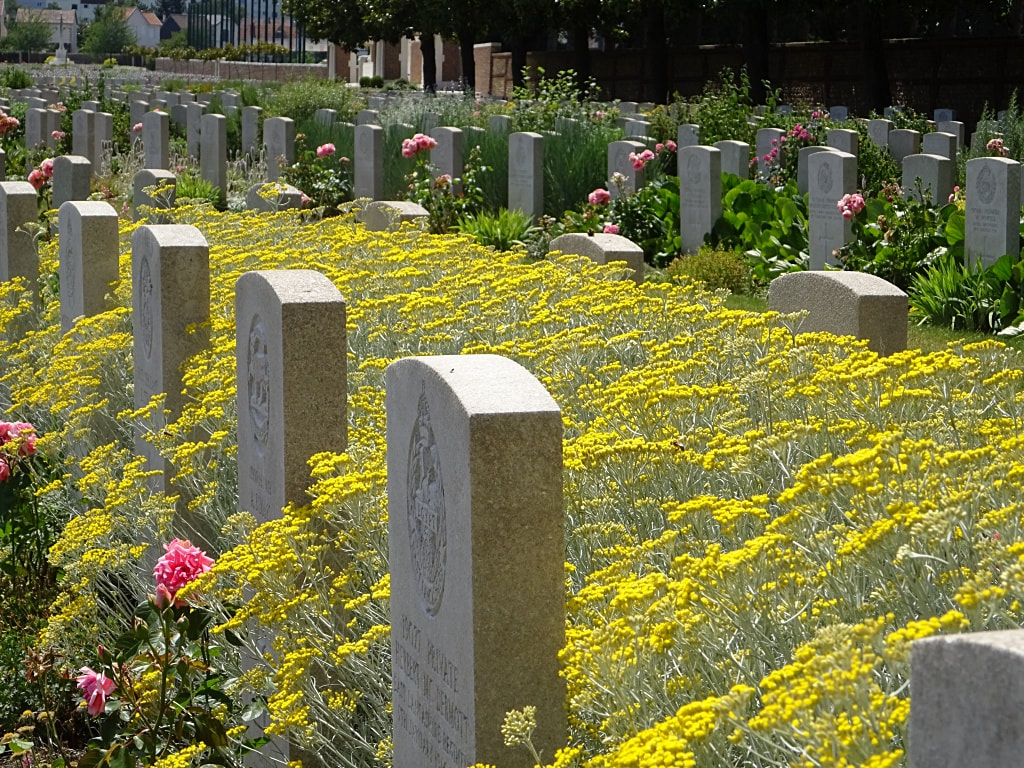
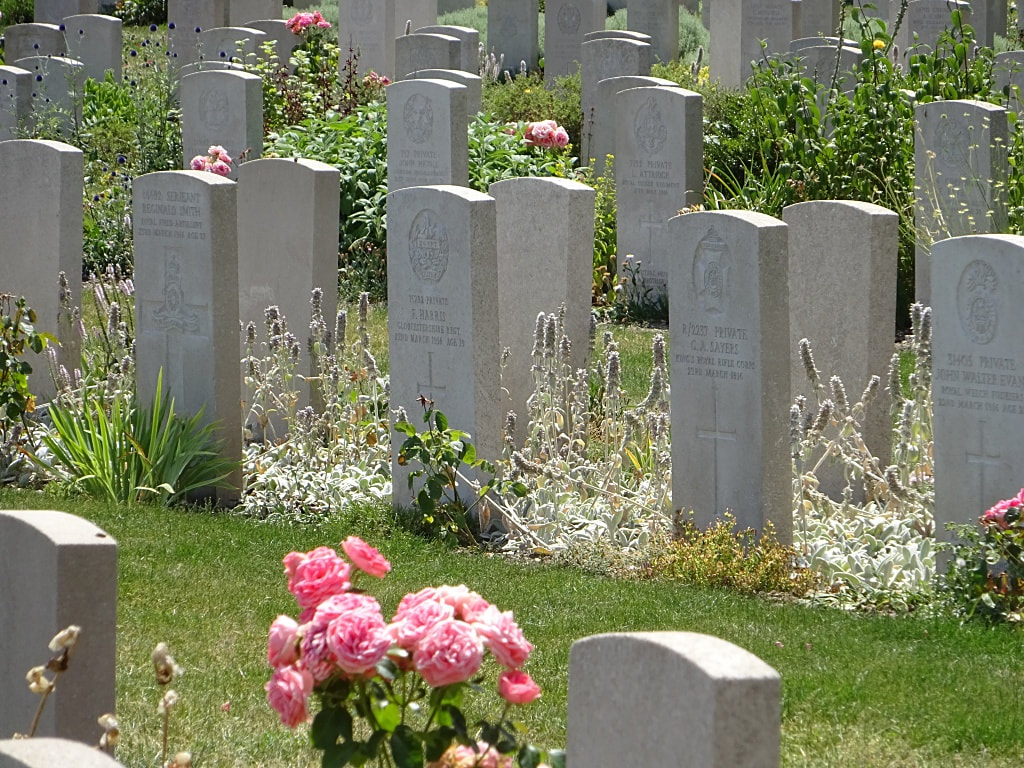
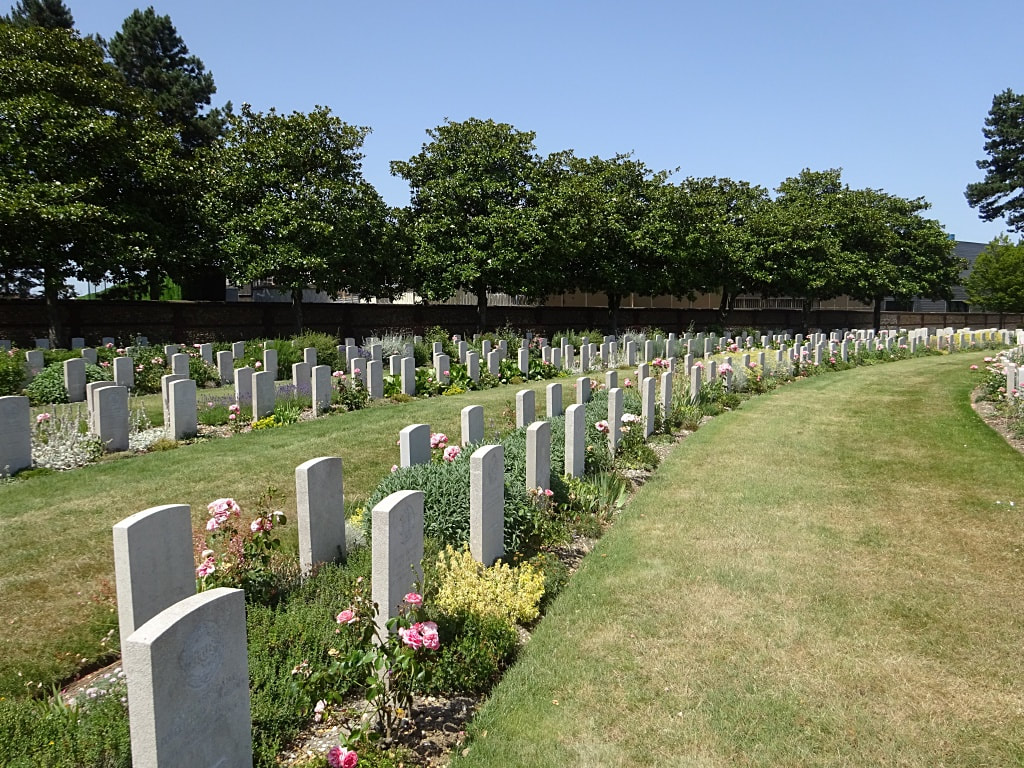
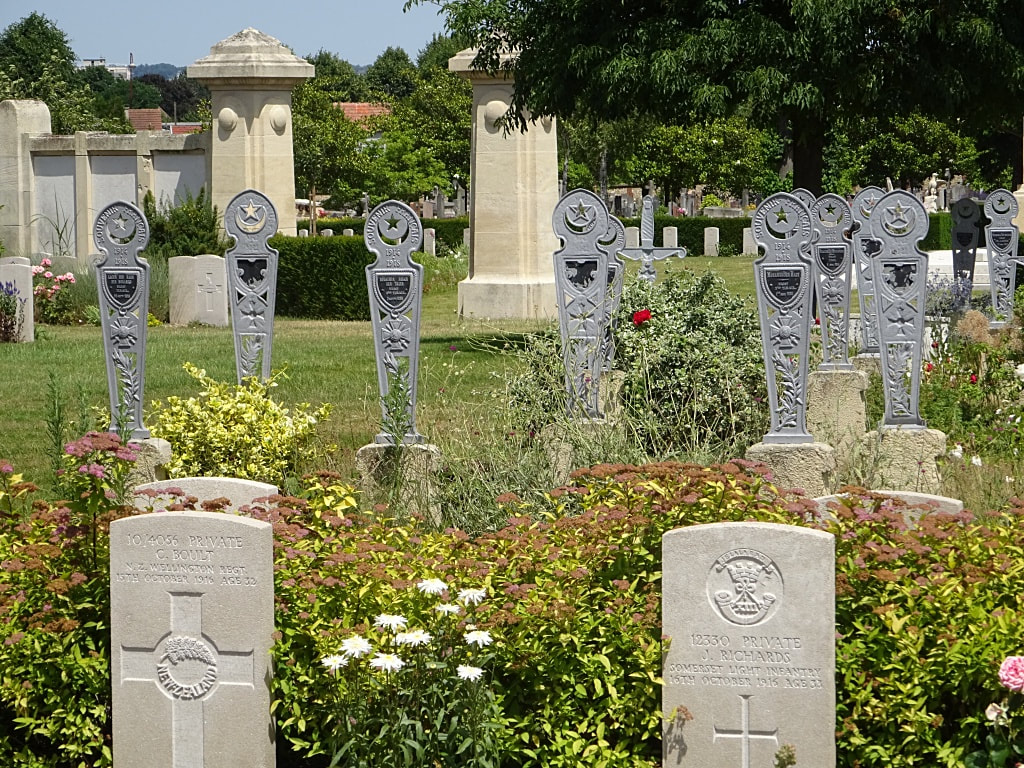
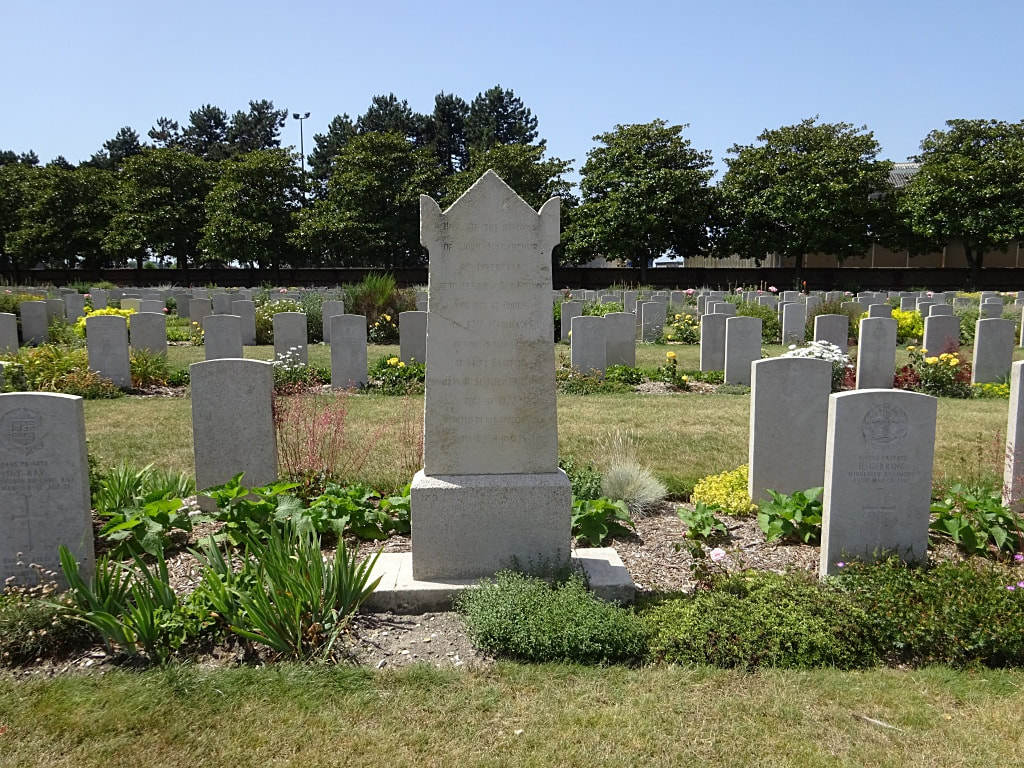
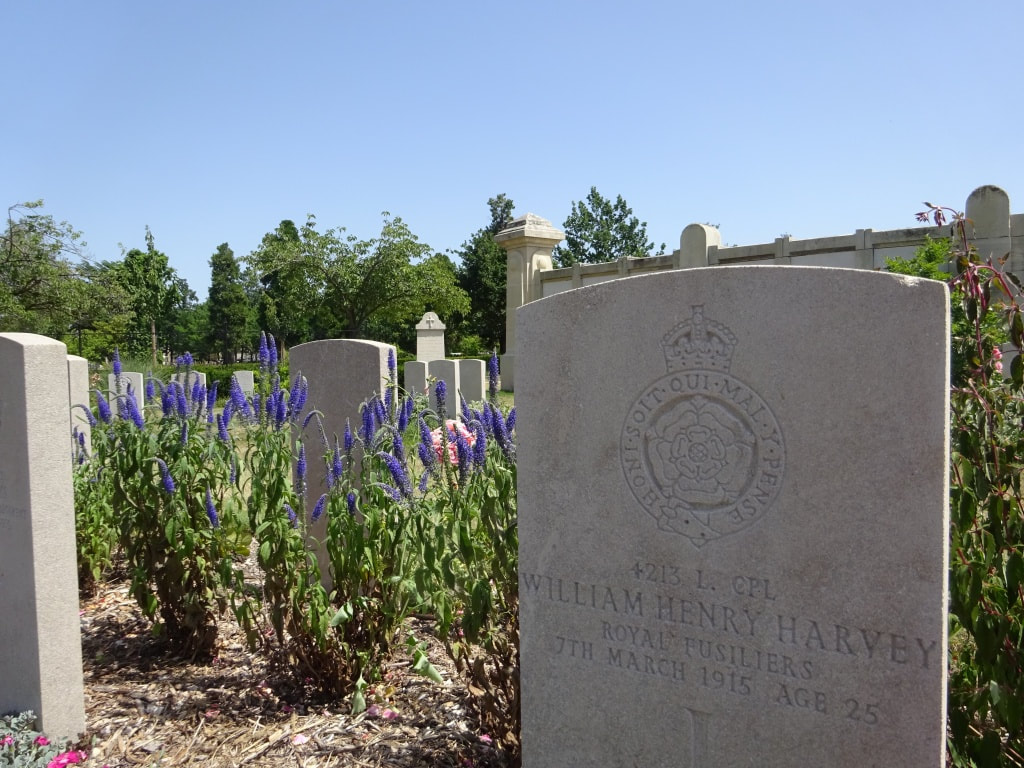
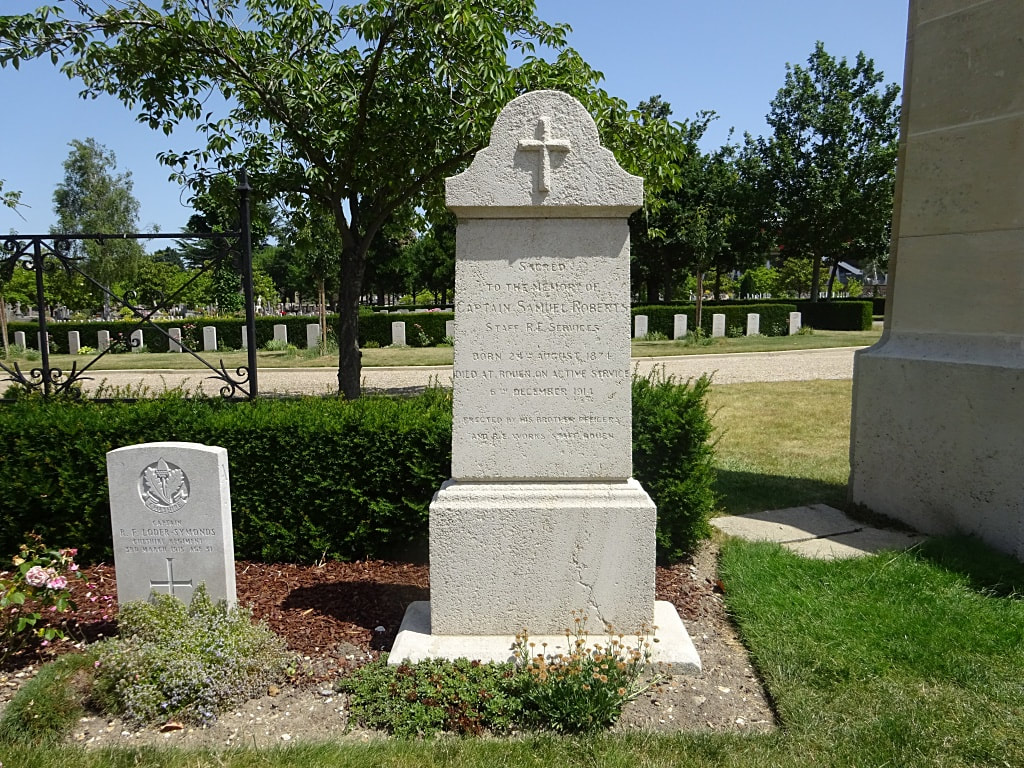
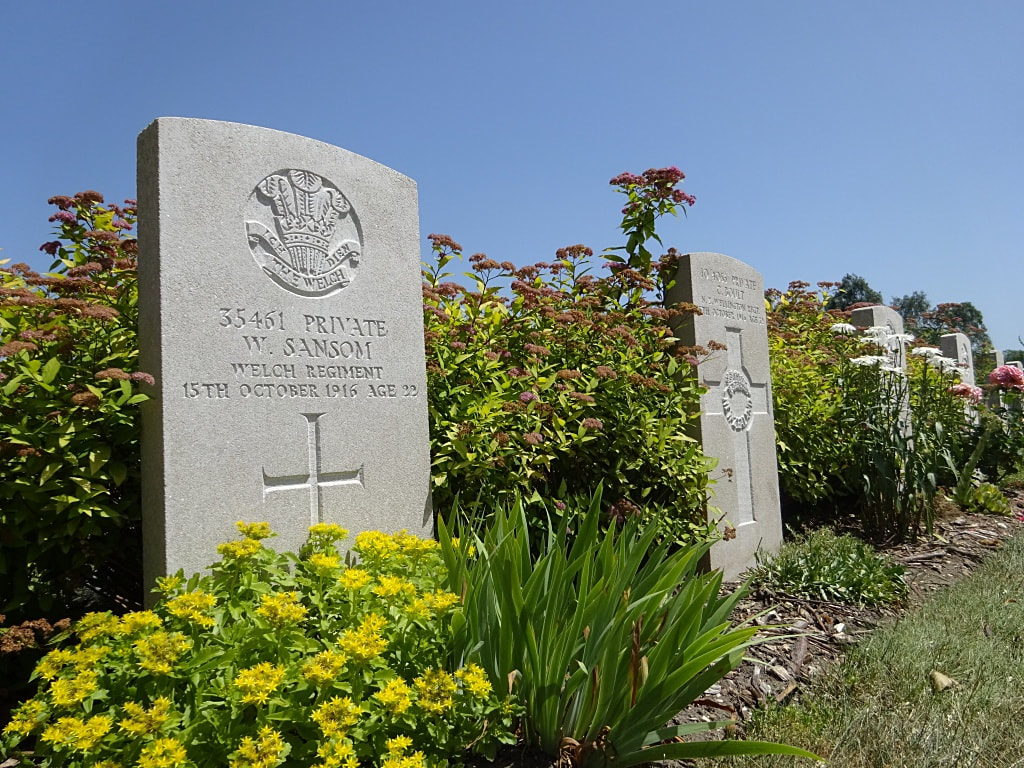
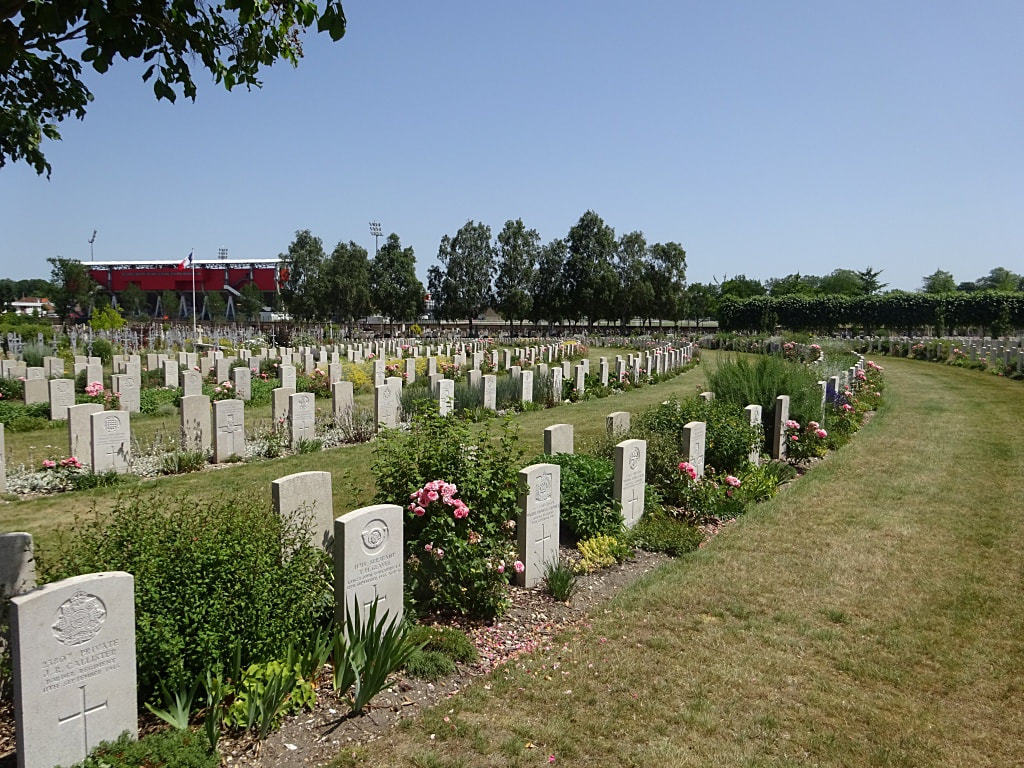
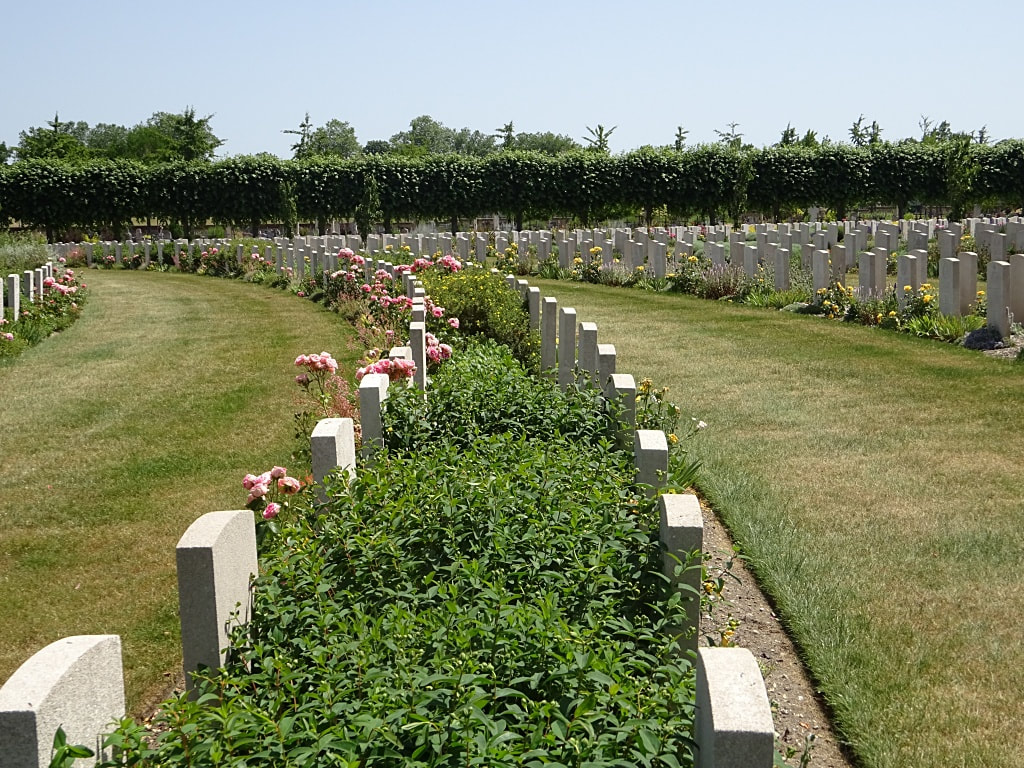
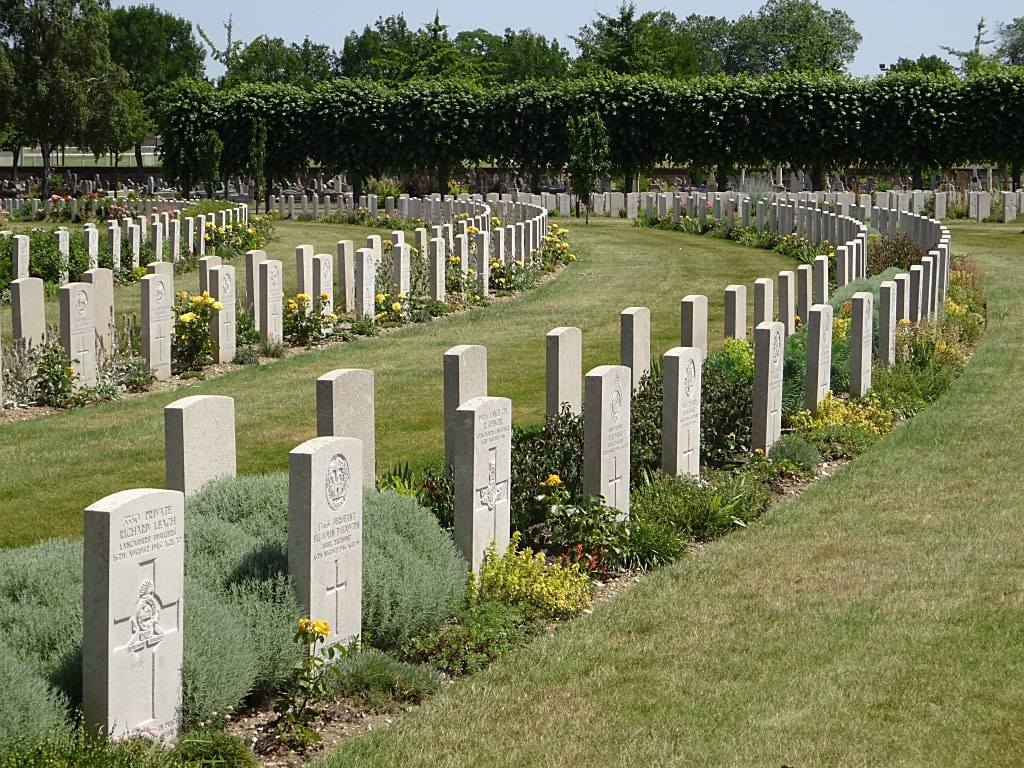
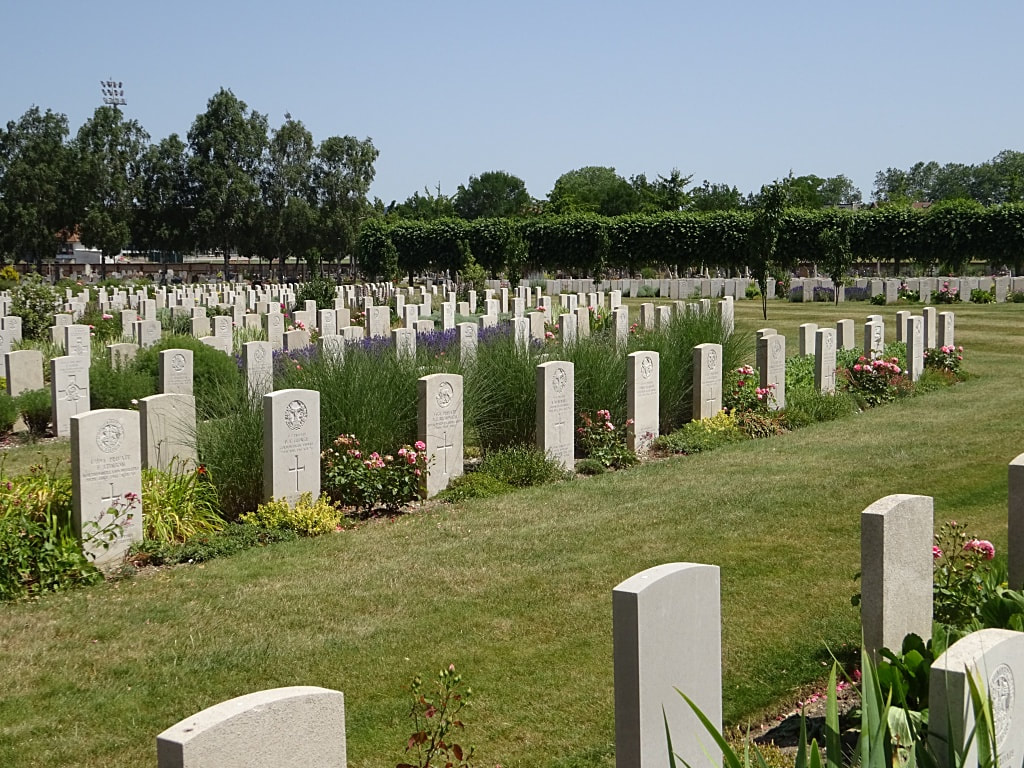
St. Sever Cemetery contains 3,082 Commonwealth burials of the First World War. There is also 1 French burial and 1 non war service burial here.The adjoining cemetery extension contains 8,348 Commonwealth burials of the First World War (ten of them unidentified) and in Block "S" there are 328 from the Second World War (18 of them unidentified). There are also 8 Foreign National burials here.
Total Burials: 3,083
World War One Commonwealth Identified Casualties: United Kingdom 2,685, Canada 137, Australia 113, India 74, New Zealand 51, South Africa 19. Total 3,079.
World War One Unidentified Casualties: United Kingdom 2.
Other Burials: France 1, Non War Service 1. Total 2.
The Commonwealth plots were designed by Sir Reginald Blomfield and Arthur James Scott Hutton
St Sever Cemetery and St Sever Cemetery Extension are located within a large communal cemetery situated on the eastern edge of the southern Rouen suburbs of Le Grand Quevilly and Le Petit Quevilly.
If approaching Rouen from the north, head for the centre of town and cross over the river Seine, following signs for Caen. Follow this route until you get to the 'Rond Point des Bruyeres' roundabout (next to the football stadium), then take the first exit into the Boulevard Stanislas Girardin. The cemetery is 150 metres down this road on the left.
If approaching Rouen from the south, follow the D938 (Avenue des Canadiens) towards the centre of town. At the 'Rond Point des Bruyeres' roundabout (next to the football stadium), take the fourth exit into the Boulevard Stanislas Girardin. The cemetery is 150 metres down this road on the left.
If arriving on foot, the easiest option is to take the Metro to the stop Charles De Gaulle in the Petit-Quevilly area and then walk east along the Boulevard Stanislas Girandin.
Visiting Information
OPENING TIMES
1 March - 1 November:
Monday-Saturday: 0815 - 1745
Sundays/Public Holidays : 0815 - 1745
2 November-28 February:
Every Day: 0815 - 1645
Historical Information
During the First World War, Commonwealth camps and hospitals were stationed on the southern outskirts of Rouen. A base supply depot and the 3rd Echelon of General Headquarters were also established in the city.
Almost all of the hospitals at Rouen remained there for practically the whole of the war. They included eight general, five stationary, one British Red Cross, one labour hospital, and No. 2 Convalescent Depot. A number of the dead from these hospitals were buried in other cemeteries, but the great majority were taken to the city cemetery of St. Sever. In September 1916, it was found necessary to begin an extension.
St. Sever Cemetery contains 3,082 Commonwealth burials of the First World War. There is also 1 French burial and 1 non war service burial here.The adjoining cemetery extension contains 8,348 Commonwealth burials of the First World War (ten of them unidentified) and in Block "S" there are 328 from the Second World War (18 of them unidentified). There are also 8 Foreign National burials here.
Total Burials: 3,083
World War One Commonwealth Identified Casualties: United Kingdom 2,685, Canada 137, Australia 113, India 74, New Zealand 51, South Africa 19. Total 3,079.
World War One Unidentified Casualties: United Kingdom 2.
Other Burials: France 1, Non War Service 1. Total 2.
The Commonwealth plots were designed by Sir Reginald Blomfield and Arthur James Scott Hutton
Doing their Bit - The Voluntary Aid Detachment
by Janine Lawrence
Over the centuries the history of our country has been littered with governmental mistakes and mishaps. How refreshing then, that in 1908 the new Secretary of State for War, Lord Haldane, undertook reforms in the army which were to have far-reaching effects.
He established a new part-time army of volunteers who were fully-trained soldiers in full-time jobs and who were organised on a county system. This Territorial Force became jokingly known as the 'Saturday Night Soldiers' as the young men who joined were taught to shoulder arms at weekly meetings and drills. They even attended summer camp and many 'Terriers' were at camp when war was declared in August 1914.
In 1909, with unbelievable foresight, the War Office issued a 'Scheme for the Organisation of Voluntary Aid in England and Wales' which recognised the need to provide sufficient medical backup to supplement the Territorial Force in the event of war. Ultimate efficiency would not be realised unless all voluntary aid was co-ordinated and the Territorial Associations were directed to entrust the work to the British Red Cross which had also adopted the county system of organisation. They joined up with the Order of St John of Jerusalem and thus, the organisation known as the Voluntary Aid Detachment was born.
Detachments were divided into those for men and those for women. Men's detachments numbered 56 lead by a commandant and comprising a medical officer, a quartermaster, a pharmacist and four section leaders each responsible for 12 men. They were usually responsible for transport and converting suitable buildings into hospitals and clearing stations and would also act as stretcher-bearers and male nurses if required. After enrolment the men studied first aid and were lectured in the various duties connected with transport and camps.
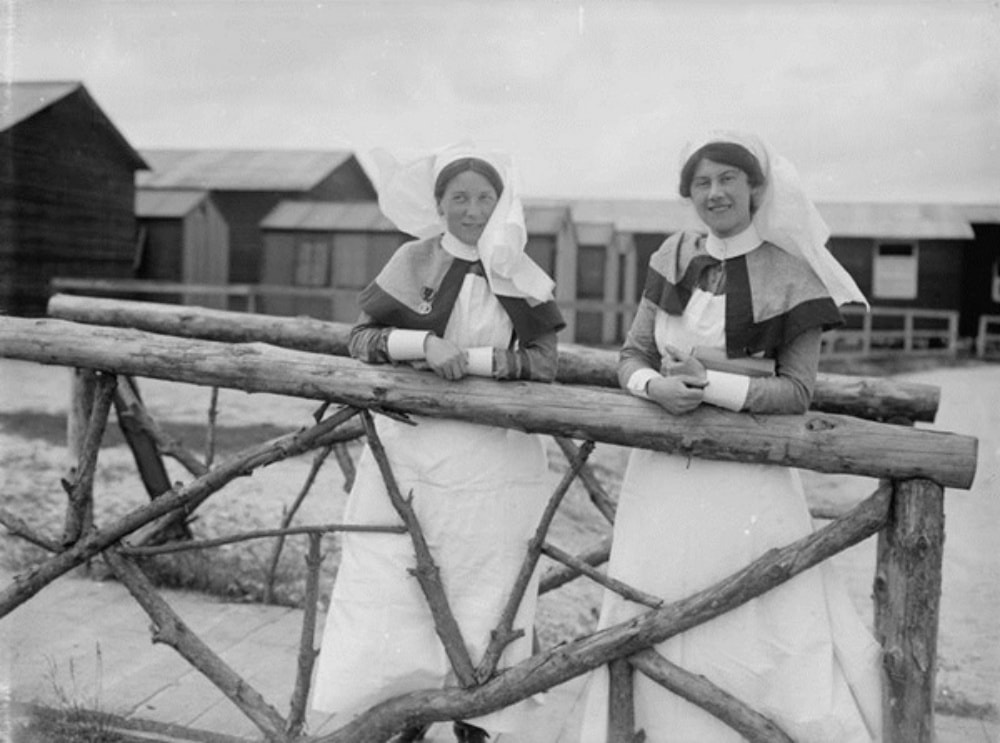
The women's detachments were less than half the strength of the men. They were also led by a commandant, who could either be male or female and not necessarily a doctor, a quartermaster, a trained nurse as a lady superintendent and 20 women of whom four had to be qualified cooks. It was felt the women's detachments would be better served to the 'less arduous' task of forming railway rest stations where they could prepare and serve meals for sick and wounded soldiers. It was obvious they were seen more as domestic assistants than nurses! However, they were given lectures in first aid, home nursing, hygiene and cookery and were occasionally given training in infirmaries. They were taught to identify suitable buildings for use as temporary hospitals and how to obtain equipment and supplies.
Within a year membership numbered somewhere around 6000 with over 2,500 detachments. These numbers increased considerably after the outbreak of war in 1914 and numbers rose to over 74,000, two-thirds of whom were women and girls.
As men were called away to answer their country's call it fell upon the women to fill their shoes in whatever way they could. Initially it was mostly middle-class women who were eager to 'do their bit' and they took on roles such as ambulance drivers, welfare officers, fundraisers, civil defence workers and even letter writers for the illiterate. It is interesting to note that the novelist, Agatha Christie was a VAD and worked in a hospital pharmacy where she learned about poisons!
The military authorities were reluctant at this early stage to accept VADs on the front line, perhaps thinking that the battlefield was no place for a woman. However, this restriction was lifted in 1915 and women volunteers over the age of twenty three and with more than three months experience were allowed to go to the Western Front, Gallipoli and Mesopotamia. Eventually VAD's were also sent to the Eastern Front.
Before the outbreak of war some VADs had taken short nursing courses for which they were awarded certificates. Qualified nurses had undertaken three years training and were understandably suspicious of these short courses, referring to the volunteers as 'ignorant amateurs'. Quarrels broke out and there are even reports of open conflict before the new spirit of unity in time of war was felt and working together for mutual benefit was the order of the day.
The VAD's became very active in the war effort using influence to transport themselves to the conflicts in France to care for the sick and wounded and thus carving out for themselves a clear role as nurses or orderlies in hospitals at home and in the theatres of war. By 1916 their numbers had increased to 80,000.
In 1917 clear regulations were laid down by the British Red Cross which governed the employment of nursing VAD's in military hospitals. Age limits were specified and volunteers should be between 21 and 48 years of age for home service and 23 and 42 for foreign. They were to be appointed for one month on probation during which time they were assessed for suitability by the matron. They then had to sign an agreement to serve for six months or the duration of the war, at home or abroad. Salary would be £20 per annum rising to £22.10.0 for those who signed on for another six months at the end of their current contract. Increments of a further £2.10.0 would be paid every six months until probationers reached the maximum of £30 per annum.
It was also laid down that VAD's should work under fully trained nurses with duties including sweeping, dusting, polishing, cleaning, washing patients' crockery, sorting linen and any nursing duties allotted by the matron.
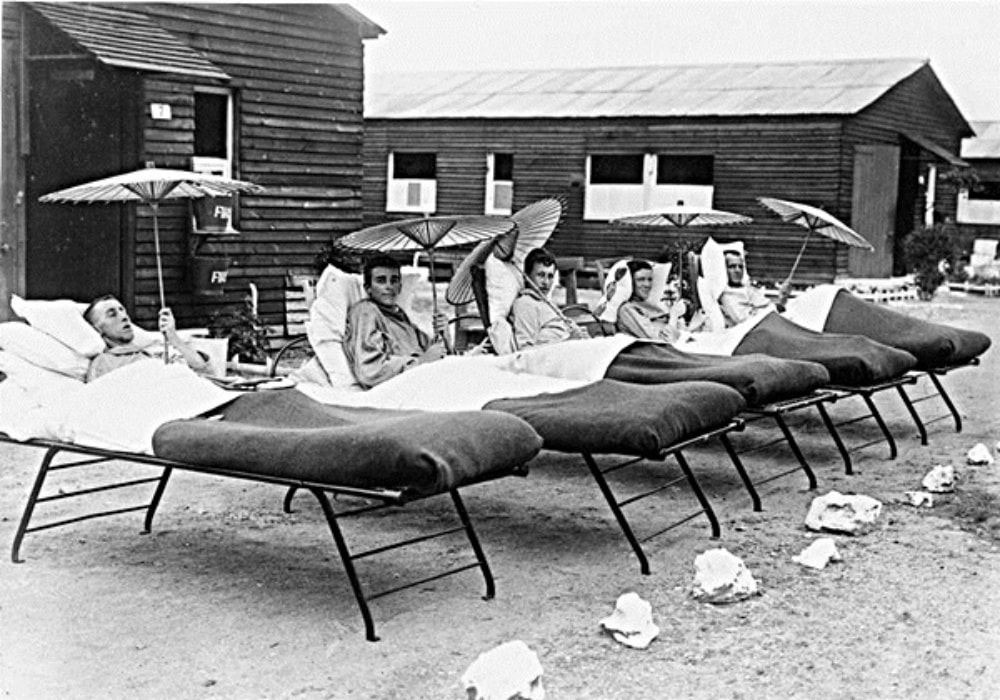
Meanwhile, VAD hospitals were being set up in Blighty and were mostly located in large houses loaned for the purpose by their owners. Gustard Wood at Wheathampstead and The Bury at King's Walden are just two Hertfordshire premises used. The Council School in Royston and the former mental hospital, Napsbury in Colney Heath are examples of institutes put into service.
These hospitals received the sum of three shillings per day per patient from the War Office and were expected to raise additional funds themselves. As everyone was keen to be seen to help the war effort this was not difficult and local newspapers regularly featured lists of donations received - obviously anonymity did not seem to be the case!
Many women returning home after the conflict ended undertook formal nurse training and registration with the General Nursing Council. Others tried to pick up the threads of their former lives. What must be certain is that life could never have been the same for any of them again. The sight, smell and fear of war must have been imprinted on every mind bringing about a change in the lives of women which would grow and grow over the following years.
Our thanks to Janine Lawrence for permission to use this article.
© Janine Lawrence
by Janine Lawrence
Over the centuries the history of our country has been littered with governmental mistakes and mishaps. How refreshing then, that in 1908 the new Secretary of State for War, Lord Haldane, undertook reforms in the army which were to have far-reaching effects.
He established a new part-time army of volunteers who were fully-trained soldiers in full-time jobs and who were organised on a county system. This Territorial Force became jokingly known as the 'Saturday Night Soldiers' as the young men who joined were taught to shoulder arms at weekly meetings and drills. They even attended summer camp and many 'Terriers' were at camp when war was declared in August 1914.
In 1909, with unbelievable foresight, the War Office issued a 'Scheme for the Organisation of Voluntary Aid in England and Wales' which recognised the need to provide sufficient medical backup to supplement the Territorial Force in the event of war. Ultimate efficiency would not be realised unless all voluntary aid was co-ordinated and the Territorial Associations were directed to entrust the work to the British Red Cross which had also adopted the county system of organisation. They joined up with the Order of St John of Jerusalem and thus, the organisation known as the Voluntary Aid Detachment was born.
Detachments were divided into those for men and those for women. Men's detachments numbered 56 lead by a commandant and comprising a medical officer, a quartermaster, a pharmacist and four section leaders each responsible for 12 men. They were usually responsible for transport and converting suitable buildings into hospitals and clearing stations and would also act as stretcher-bearers and male nurses if required. After enrolment the men studied first aid and were lectured in the various duties connected with transport and camps.
The women's detachments were less than half the strength of the men. They were also led by a commandant, who could either be male or female and not necessarily a doctor, a quartermaster, a trained nurse as a lady superintendent and 20 women of whom four had to be qualified cooks. It was felt the women's detachments would be better served to the 'less arduous' task of forming railway rest stations where they could prepare and serve meals for sick and wounded soldiers. It was obvious they were seen more as domestic assistants than nurses! However, they were given lectures in first aid, home nursing, hygiene and cookery and were occasionally given training in infirmaries. They were taught to identify suitable buildings for use as temporary hospitals and how to obtain equipment and supplies.
Within a year membership numbered somewhere around 6000 with over 2,500 detachments. These numbers increased considerably after the outbreak of war in 1914 and numbers rose to over 74,000, two-thirds of whom were women and girls.
As men were called away to answer their country's call it fell upon the women to fill their shoes in whatever way they could. Initially it was mostly middle-class women who were eager to 'do their bit' and they took on roles such as ambulance drivers, welfare officers, fundraisers, civil defence workers and even letter writers for the illiterate. It is interesting to note that the novelist, Agatha Christie was a VAD and worked in a hospital pharmacy where she learned about poisons!
The military authorities were reluctant at this early stage to accept VADs on the front line, perhaps thinking that the battlefield was no place for a woman. However, this restriction was lifted in 1915 and women volunteers over the age of twenty three and with more than three months experience were allowed to go to the Western Front, Gallipoli and Mesopotamia. Eventually VAD's were also sent to the Eastern Front.
Before the outbreak of war some VADs had taken short nursing courses for which they were awarded certificates. Qualified nurses had undertaken three years training and were understandably suspicious of these short courses, referring to the volunteers as 'ignorant amateurs'. Quarrels broke out and there are even reports of open conflict before the new spirit of unity in time of war was felt and working together for mutual benefit was the order of the day.
The VAD's became very active in the war effort using influence to transport themselves to the conflicts in France to care for the sick and wounded and thus carving out for themselves a clear role as nurses or orderlies in hospitals at home and in the theatres of war. By 1916 their numbers had increased to 80,000.
In 1917 clear regulations were laid down by the British Red Cross which governed the employment of nursing VAD's in military hospitals. Age limits were specified and volunteers should be between 21 and 48 years of age for home service and 23 and 42 for foreign. They were to be appointed for one month on probation during which time they were assessed for suitability by the matron. They then had to sign an agreement to serve for six months or the duration of the war, at home or abroad. Salary would be £20 per annum rising to £22.10.0 for those who signed on for another six months at the end of their current contract. Increments of a further £2.10.0 would be paid every six months until probationers reached the maximum of £30 per annum.
It was also laid down that VAD's should work under fully trained nurses with duties including sweeping, dusting, polishing, cleaning, washing patients' crockery, sorting linen and any nursing duties allotted by the matron.
Meanwhile, VAD hospitals were being set up in Blighty and were mostly located in large houses loaned for the purpose by their owners. Gustard Wood at Wheathampstead and The Bury at King's Walden are just two Hertfordshire premises used. The Council School in Royston and the former mental hospital, Napsbury in Colney Heath are examples of institutes put into service.
These hospitals received the sum of three shillings per day per patient from the War Office and were expected to raise additional funds themselves. As everyone was keen to be seen to help the war effort this was not difficult and local newspapers regularly featured lists of donations received - obviously anonymity did not seem to be the case!
Many women returning home after the conflict ended undertook formal nurse training and registration with the General Nursing Council. Others tried to pick up the threads of their former lives. What must be certain is that life could never have been the same for any of them again. The sight, smell and fear of war must have been imprinted on every mind bringing about a change in the lives of women which would grow and grow over the following years.
Our thanks to Janine Lawrence for permission to use this article.
© Janine Lawrence