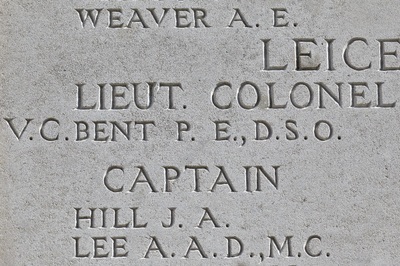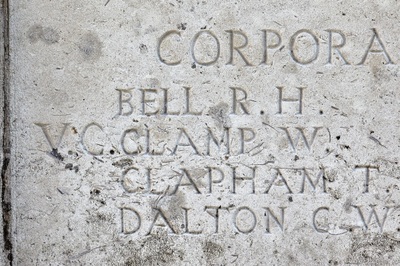TYNE COT MEMORIAL
West-Vlaanderen
Belgium
GPS: Latitude 50.887279, Longitude 2.999485
Roll of Honour
Listed by Surname
Location Information
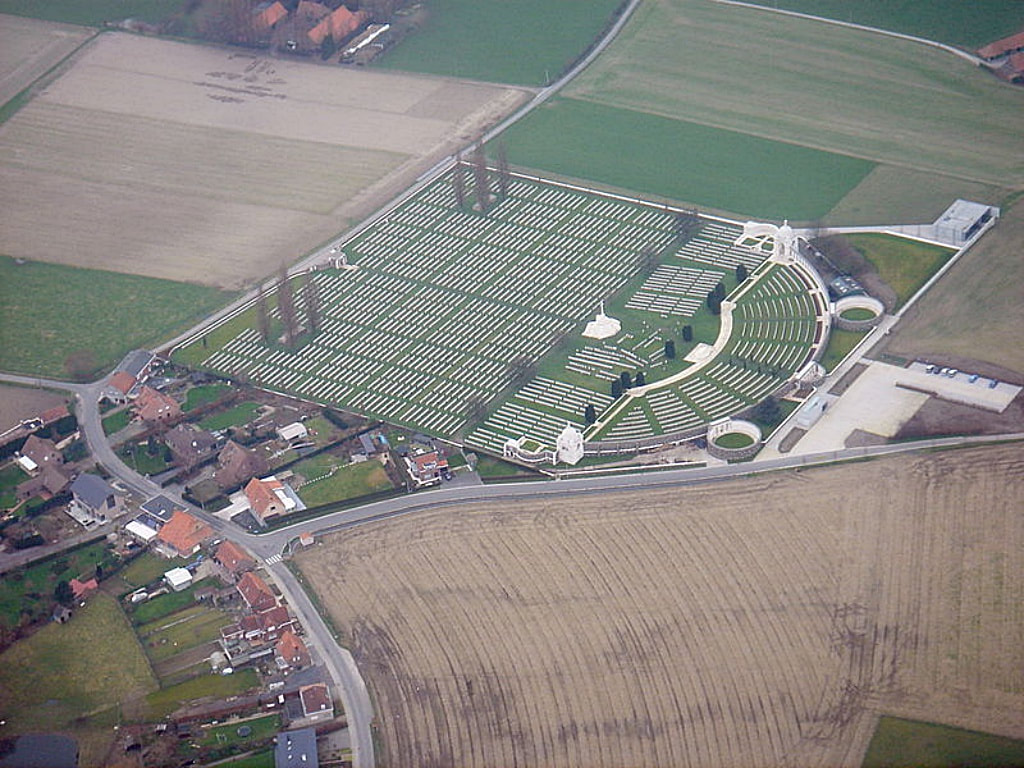
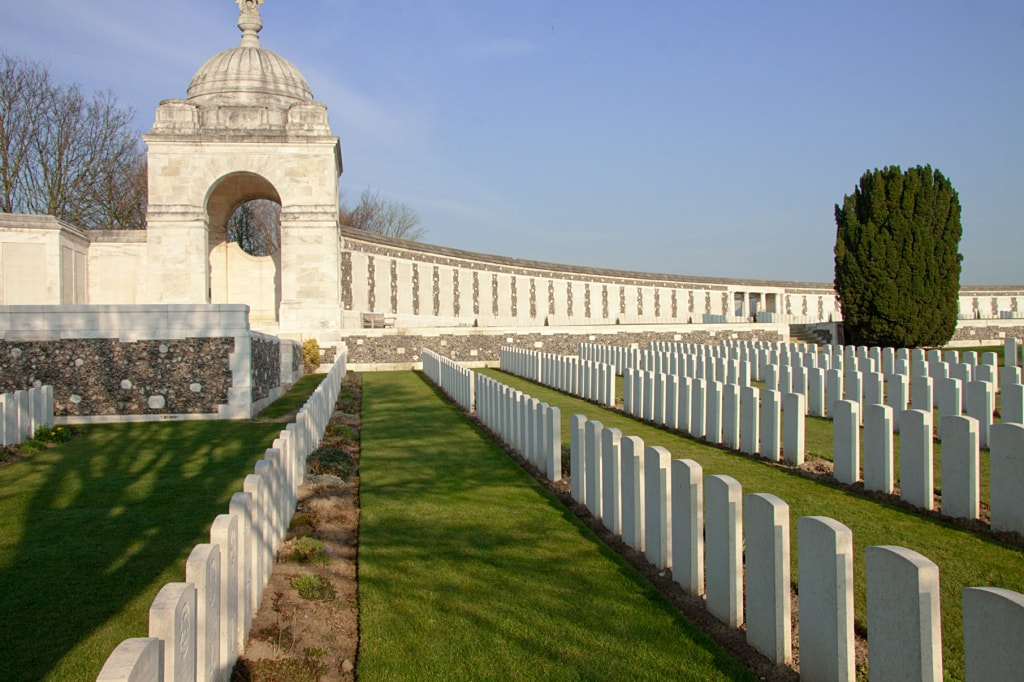
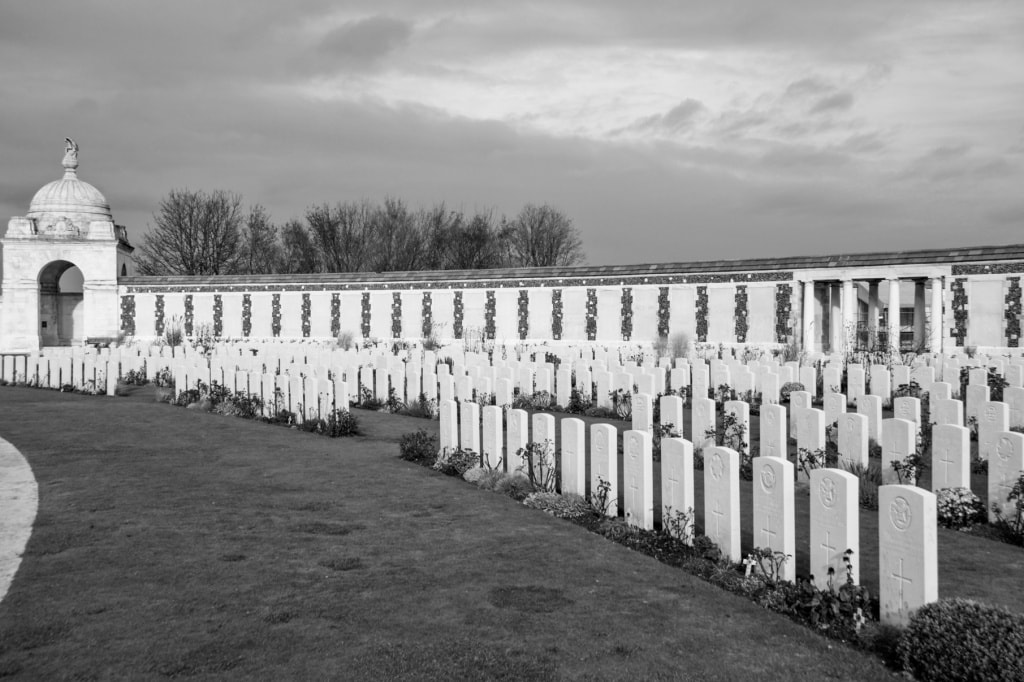
The Tyne Cot Memorial to the Missing forms the north-eastern boundary of Tyne Cot Cemetery, which is located 9 kilometres north east of Ieper town centre, on the Tynecotstraat, a road leading from the Zonnebeekseweg (N332).
The names of those from United Kingdom units are inscribed on Panels arranged by Regiment under their respective Ranks.
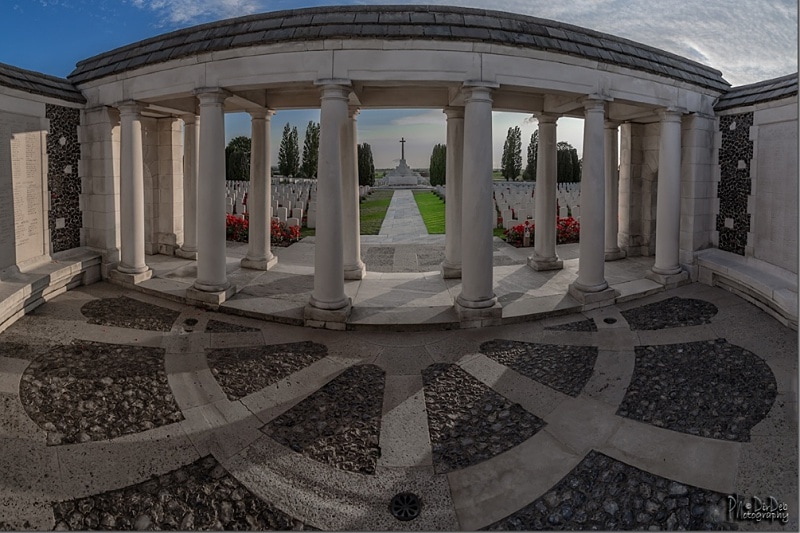
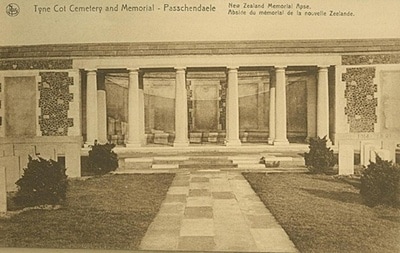
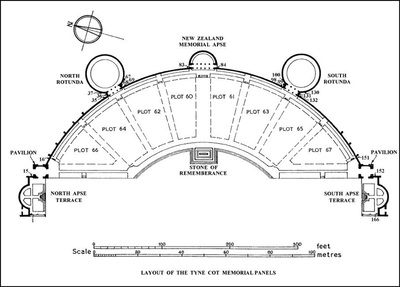
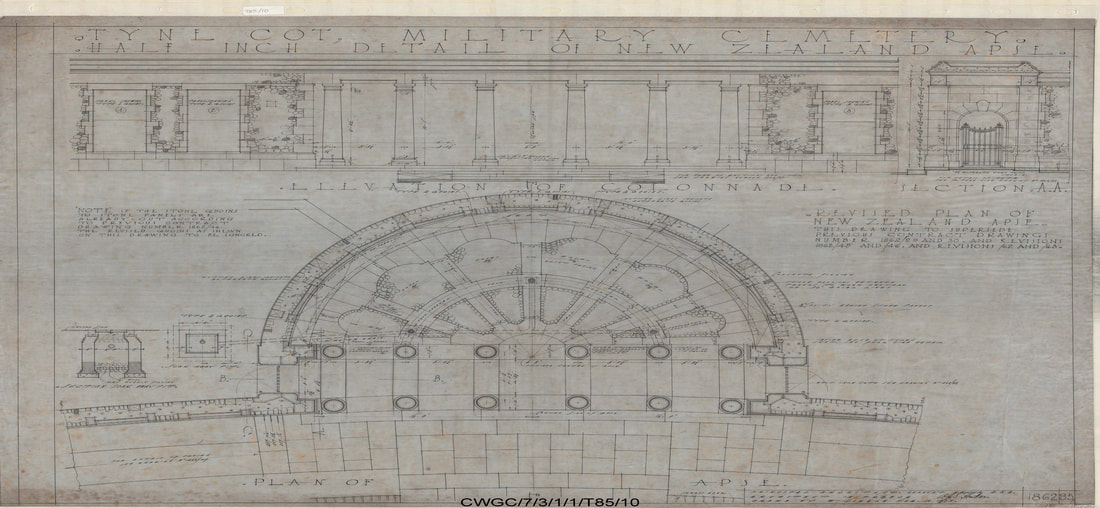
The names of those from New Zealand units are inscribed on panels within the New Zealand Memorial Apse located at the centre of the Memorial.
Visiting Information
There are two separate registers for this site - one for the cemetery and one for the memorial. The cemetery register will be found in the gatehouse as you enter the cemetery, and the memorial register will be found in the left hand rotunda of the memorial as you face the memorial. SCHOOL GROUPS: TEACHERS - PLEASE CLOSELY SUPERVISE YOUR STUDENTS, PARTICULARLY AT THE TYNE COT CEMETERY CROSS OF SACRIFICE Wheelchair access to this cemetery is possible via an entrance at the rear and is signposted from the car park.
Panel Numbers quoted at the end of each entry relate to the panels dedicated to the Regiment with which the casualty served. In some instances, where a casualty is recorded as attached to another Regiment, his name may appear within their Regimental Panels. Please refer to the on-site Memorial Register Introduction. The Addenda Panel lists those service personnel whose details are awaiting addition to the Regimental Panels.
Wheelchair access to this cemetery is possible via an entrance at the rear and is signposted from the car park.
Historical Information
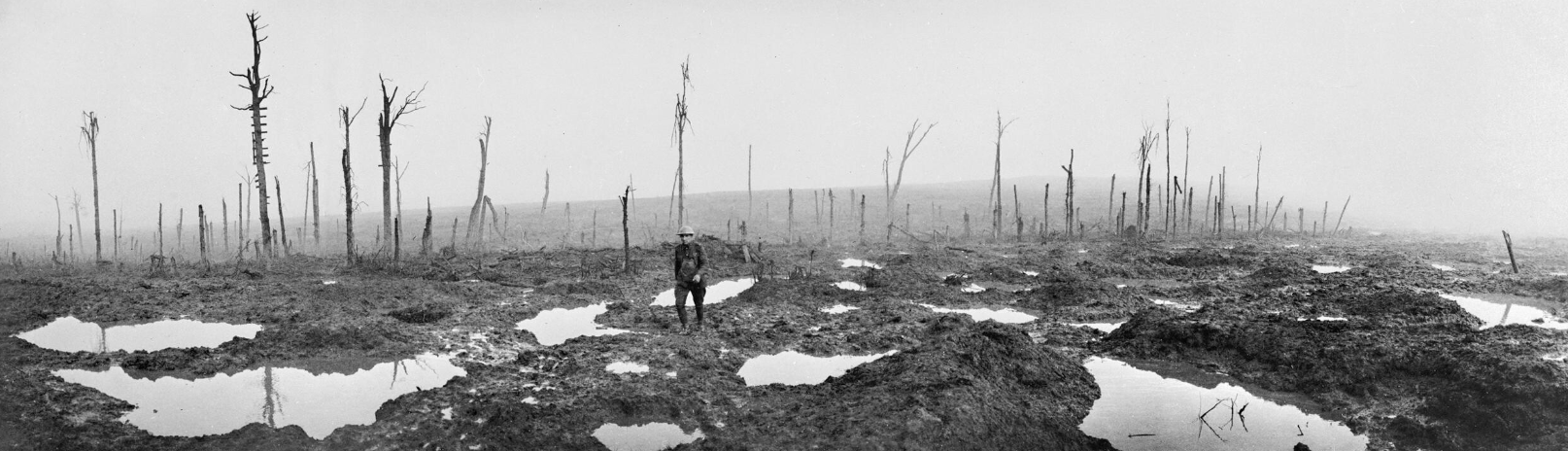
The Tyne Cot Memorial is one of four memorials to the missing in Belgian Flanders which cover the area known as the Ypres Salient. Broadly speaking, the Salient stretched from Langemarck in the north to the northern edge in Ploegsteert Wood in the south, but it varied in area and shape throughout the war.
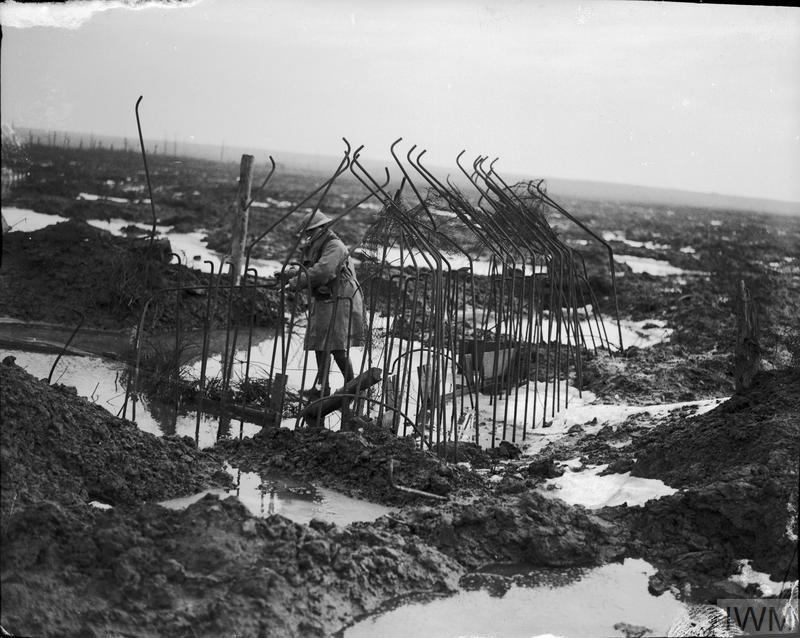
The Salient was formed during the First Battle of Ypres in October and November 1914, when a small British Expeditionary Force succeeded in securing the town before the onset of winter, pushing the German forces back to the Passchendaele Ridge. The Second Battle of Ypres began in April 1915 when the Germans released poison gas into the Allied lines north of Ypres. This was the first time gas had been used by either side and the violence of the attack forced an Allied withdrawal and a shortening of the line of defence.
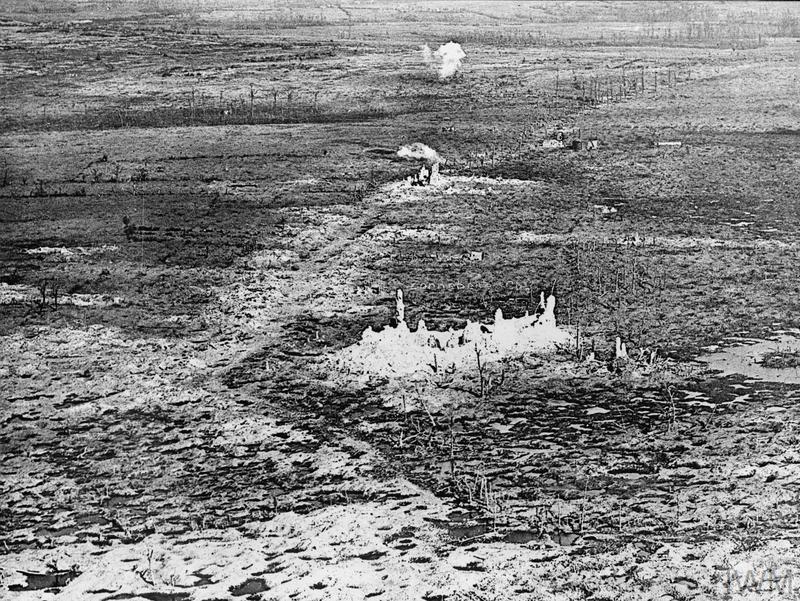
There was little more significant activity on this front until 1917, when in the Third Battle of Ypres an offensive was mounted by Commonwealth forces to divert German attention from a weakened French front further south. The initial attempt in June to dislodge the Germans from the Messines Ridge was a complete success, but the main assault north-eastward, which began at the end of July, quickly became a dogged struggle against determined opposition and the rapidly deteriorating weather. The campaign finally came to a close in November with the capture of Passchendaele.
The German offensive of March 1918 met with some initial success, but was eventually checked and repulsed in a combined effort by the Allies in September.
The battles of the Ypres Salient claimed many lives on both sides and it quickly became clear that the commemoration of members of the Commonwealth forces with no known grave would have to be divided between several different sites.
The site of the Menin Gate was chosen because of the hundreds of thousands of men who passed through it on their way to the battlefields. It commemorates those of all Commonwealth nations, except New Zealand, who died in the Salient, in the case of United Kingdom casualties before 16 August 1917 (with some exceptions). Those United Kingdom and New Zealand servicemen who died after that date are named on the memorial at Tyne Cot, a site which marks the furthest point reached by Commonwealth forces in Belgium until nearly the end of the war. Other New Zealand casualties are commemorated on memorials at Buttes New British Cemetery and Messines Ridge British Cemetery.
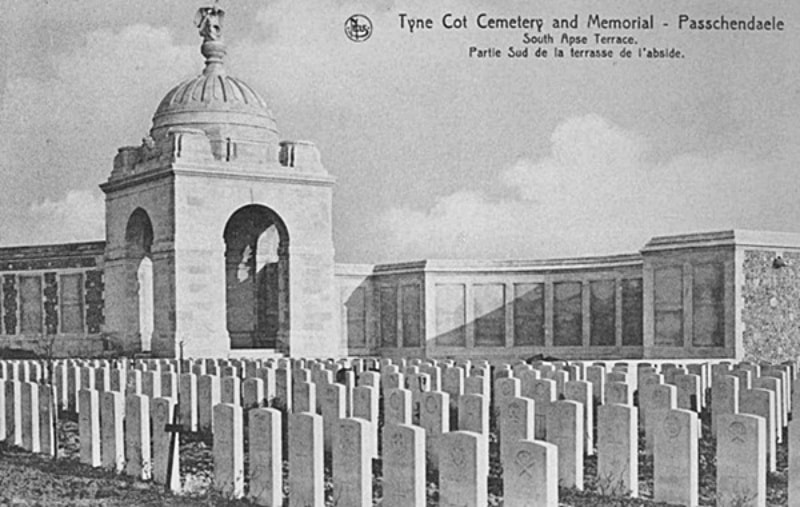
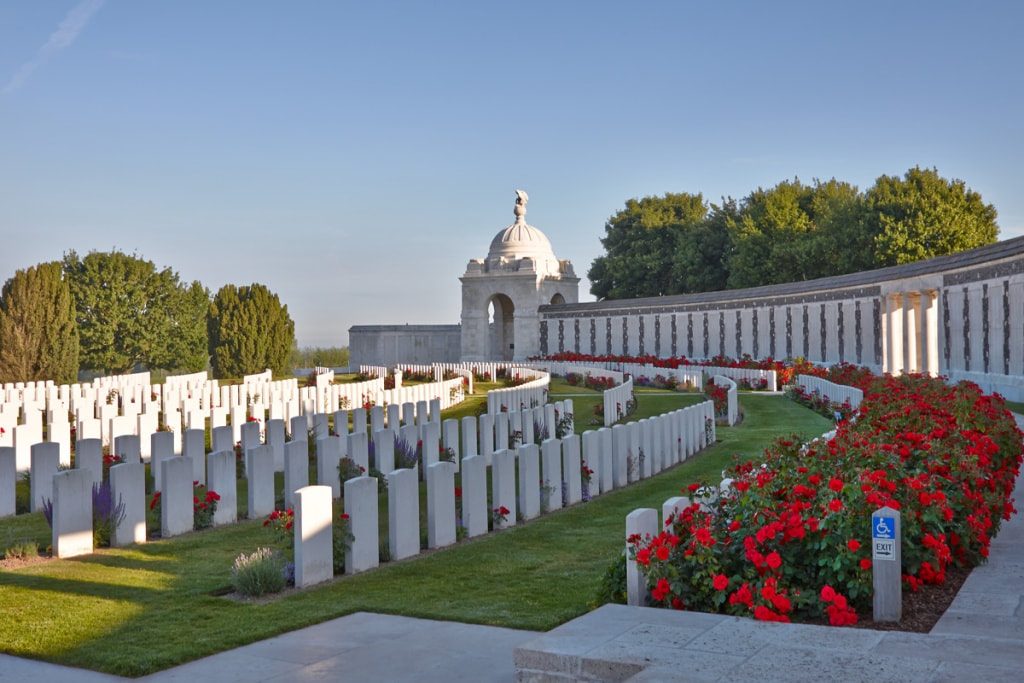
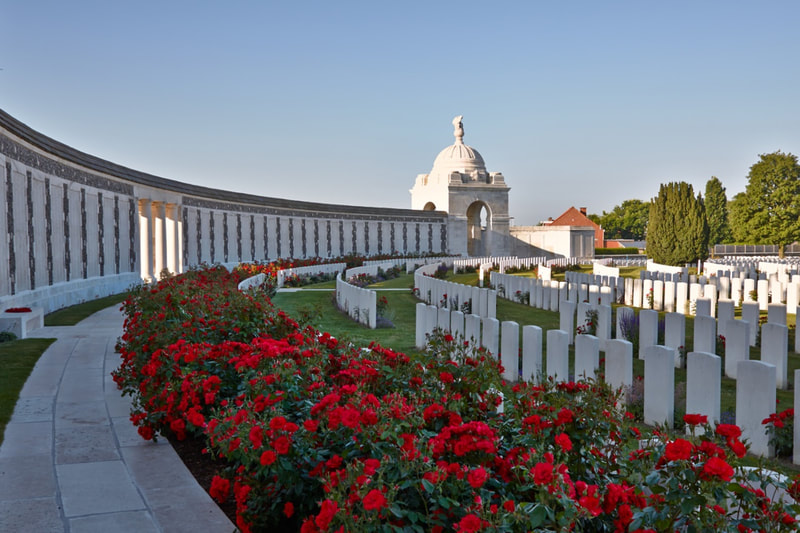
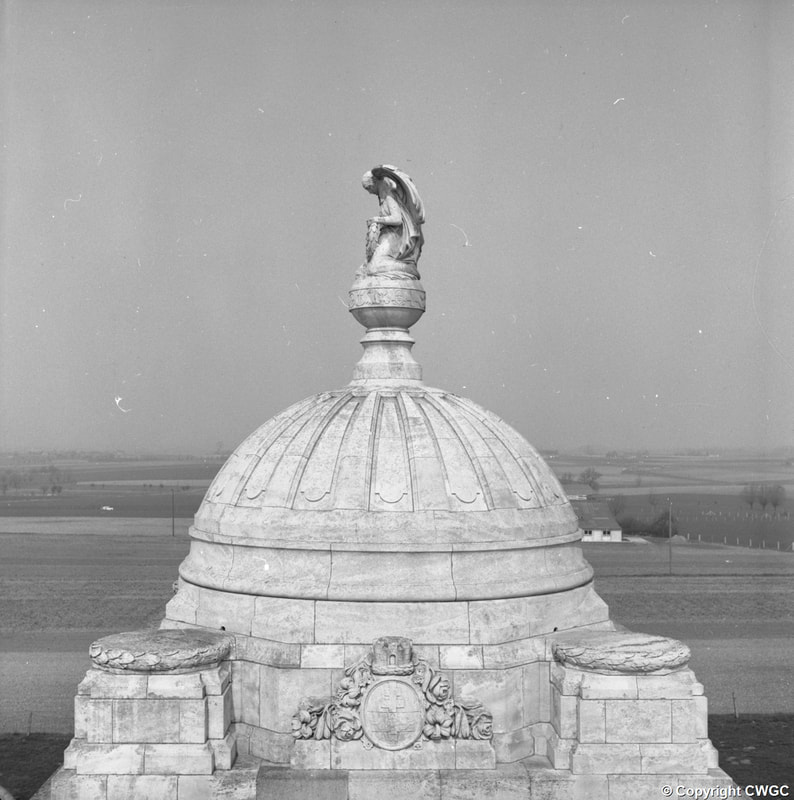
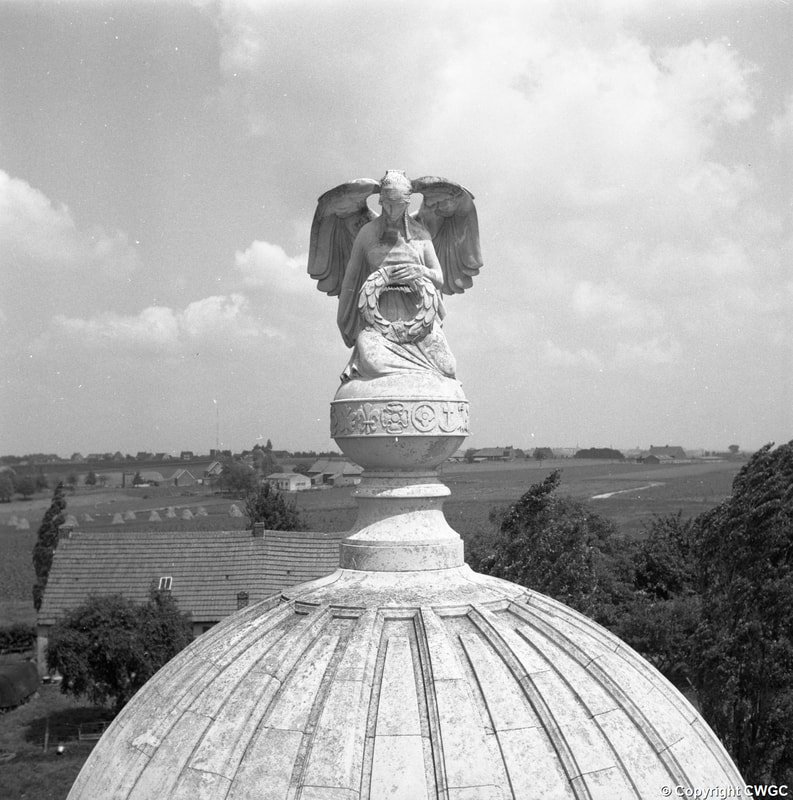
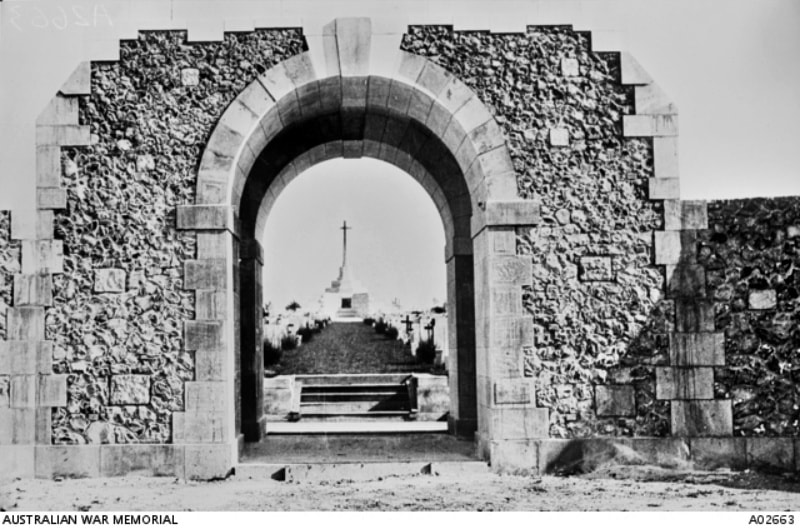
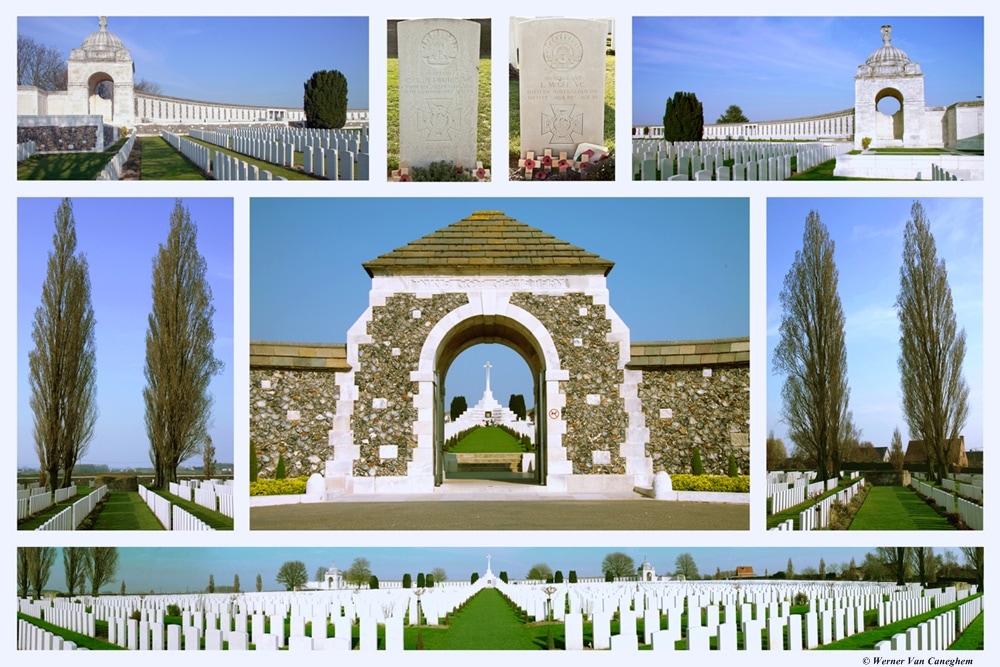
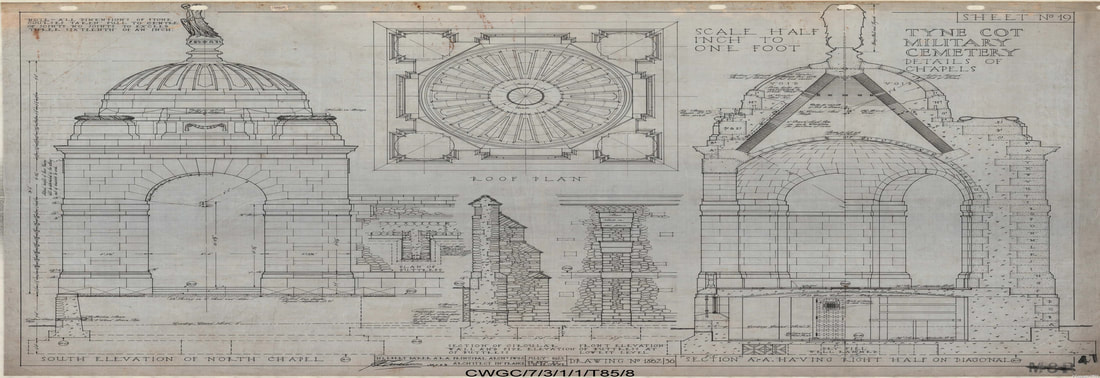
The TYNE COT MEMORIAL now bears the names of 34,948 officers and men whose graves are not known. The memorial, designed by Sir Herbert Baker with sculpture by Joseph Armitage and F.V. Blundstone, was unveiled by Sir Gilbert Dyett on 20 June 1927.
Commemorated: United Kingdom 33,783, New Zealand 1,165. Total 34,948.
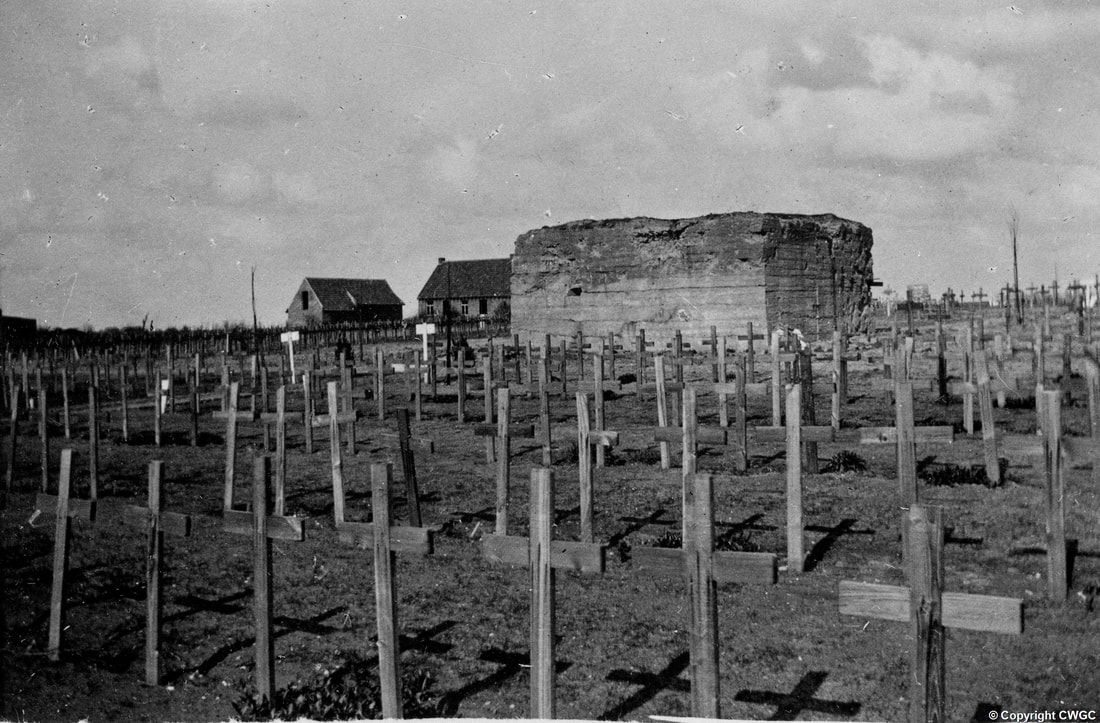
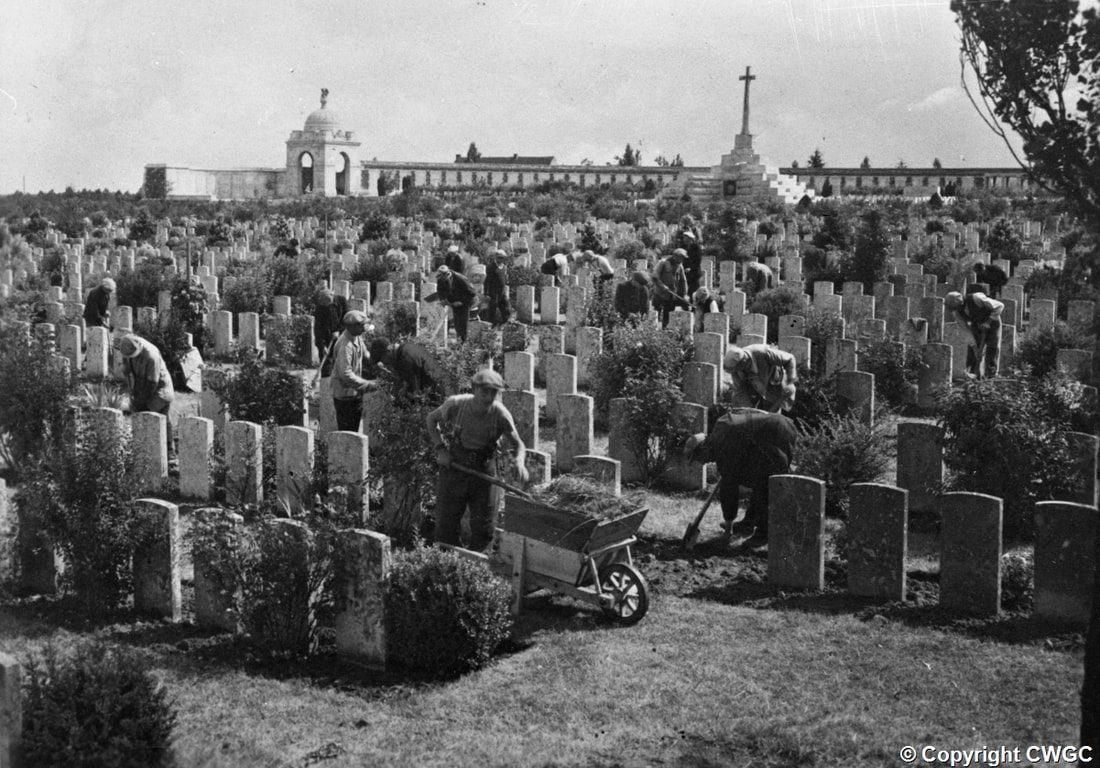
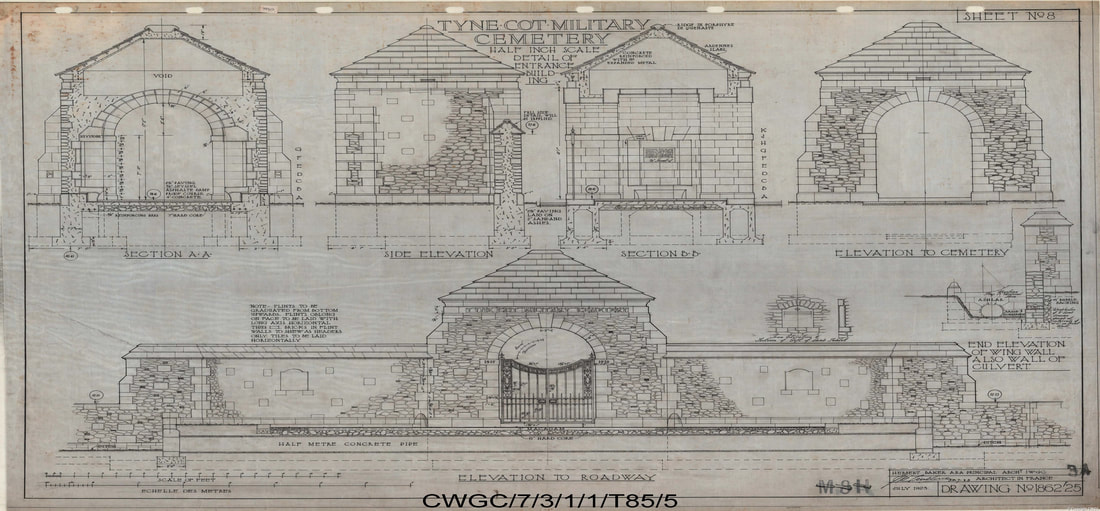
The memorial forms the north-eastern boundary of TYNE COT CEMETERY, which was established around a captured German blockhouse or pill-box used as an advanced dressing station. The original battlefield cemetery of 343 graves was greatly enlarged after the Armistice when remains were brought in from the battlefields of Passchendaele and Langemarck, and from a few small burial grounds. It is now the largest Commonwealth war cemetery in the world in terms of burials. At the suggestion of King George V, who visited the cemetery in 1922, the Cross of Sacrifice was placed on the original large pill-box. There are three other pill-boxes in the cemetery.
There are now 11,964 Commonwealth servicemen of the First World War buried or commemorated in Tyne Cot Cemetery. 8,372 of the burials are unidentified but there are special memorials to more than 80 casualties known or believed to be buried among them. Other special memorials commemorate 20 casualties whose graves were destroyed by shell fire. There are 4 German burials, 3 being unidentified.
Total Burials: 11,968.
Identified Casualties: United Kingdom 2,337, Australia 582, Canada 451, New Zealand 178, South Africa 24, Germany 1. Total 3,593.
Unidentified Casualties: 8,375.
The cemetery and Memorial was designed by Sir Herbert Bakerand John Reginald Truelove
Decorative Features: Ferdinand Blundstone and Joseph Armitage
Location Information
The Tyne Cot Memorial to the Missing forms the north-eastern boundary of Tyne Cot Cemetery, which is located 9 kilometres north east of Ieper town centre, on the Tynecotstraat, a road leading from the Zonnebeekseweg (N332).
The names of those from United Kingdom units are inscribed on Panels arranged by Regiment under their respective Ranks.
The names of those from New Zealand units are inscribed on panels within the New Zealand Memorial Apse located at the centre of the Memorial.
Visiting Information
There are two separate registers for this site - one for the cemetery and one for the memorial. The cemetery register will be found in the gatehouse as you enter the cemetery, and the memorial register will be found in the left hand rotunda of the memorial as you face the memorial. SCHOOL GROUPS: TEACHERS - PLEASE CLOSELY SUPERVISE YOUR STUDENTS, PARTICULARLY AT THE TYNE COT CEMETERY CROSS OF SACRIFICE Wheelchair access to this cemetery is possible via an entrance at the rear and is signposted from the car park.
Panel Numbers quoted at the end of each entry relate to the panels dedicated to the Regiment with which the casualty served. In some instances, where a casualty is recorded as attached to another Regiment, his name may appear within their Regimental Panels. Please refer to the on-site Memorial Register Introduction. The Addenda Panel lists those service personnel whose details are awaiting addition to the Regimental Panels.
Wheelchair access to this cemetery is possible via an entrance at the rear and is signposted from the car park.
Historical Information
The Tyne Cot Memorial is one of four memorials to the missing in Belgian Flanders which cover the area known as the Ypres Salient. Broadly speaking, the Salient stretched from Langemarck in the north to the northern edge in Ploegsteert Wood in the south, but it varied in area and shape throughout the war.
The Salient was formed during the First Battle of Ypres in October and November 1914, when a small British Expeditionary Force succeeded in securing the town before the onset of winter, pushing the German forces back to the Passchendaele Ridge. The Second Battle of Ypres began in April 1915 when the Germans released poison gas into the Allied lines north of Ypres. This was the first time gas had been used by either side and the violence of the attack forced an Allied withdrawal and a shortening of the line of defence.
There was little more significant activity on this front until 1917, when in the Third Battle of Ypres an offensive was mounted by Commonwealth forces to divert German attention from a weakened French front further south. The initial attempt in June to dislodge the Germans from the Messines Ridge was a complete success, but the main assault north-eastward, which began at the end of July, quickly became a dogged struggle against determined opposition and the rapidly deteriorating weather. The campaign finally came to a close in November with the capture of Passchendaele.
The German offensive of March 1918 met with some initial success, but was eventually checked and repulsed in a combined effort by the Allies in September.
The battles of the Ypres Salient claimed many lives on both sides and it quickly became clear that the commemoration of members of the Commonwealth forces with no known grave would have to be divided between several different sites.
The site of the Menin Gate was chosen because of the hundreds of thousands of men who passed through it on their way to the battlefields. It commemorates those of all Commonwealth nations, except New Zealand, who died in the Salient, in the case of United Kingdom casualties before 16 August 1917 (with some exceptions). Those United Kingdom and New Zealand servicemen who died after that date are named on the memorial at Tyne Cot, a site which marks the furthest point reached by Commonwealth forces in Belgium until nearly the end of the war. Other New Zealand casualties are commemorated on memorials at Buttes New British Cemetery and Messines Ridge British Cemetery.
The TYNE COT MEMORIAL now bears the names of 34,948 officers and men whose graves are not known. The memorial, designed by Sir Herbert Baker with sculpture by Joseph Armitage and F.V. Blundstone, was unveiled by Sir Gilbert Dyett on 20 June 1927.
Commemorated: United Kingdom 33,783, New Zealand 1,165. Total 34,948.
The memorial forms the north-eastern boundary of TYNE COT CEMETERY, which was established around a captured German blockhouse or pill-box used as an advanced dressing station. The original battlefield cemetery of 343 graves was greatly enlarged after the Armistice when remains were brought in from the battlefields of Passchendaele and Langemarck, and from a few small burial grounds. It is now the largest Commonwealth war cemetery in the world in terms of burials. At the suggestion of King George V, who visited the cemetery in 1922, the Cross of Sacrifice was placed on the original large pill-box. There are three other pill-boxes in the cemetery.
There are now 11,964 Commonwealth servicemen of the First World War buried or commemorated in Tyne Cot Cemetery. 8,372 of the burials are unidentified but there are special memorials to more than 80 casualties known or believed to be buried among them. Other special memorials commemorate 20 casualties whose graves were destroyed by shell fire. There are 4 German burials, 3 being unidentified.
Total Burials: 11,968.
Identified Casualties: United Kingdom 2,337, Australia 582, Canada 451, New Zealand 178, South Africa 24, Germany 1. Total 3,593.
Unidentified Casualties: 8,375.
The cemetery and Memorial was designed by Sir Herbert Bakerand John Reginald Truelove
Decorative Features: Ferdinand Blundstone and Joseph Armitage
Images in this gallery © Geerhard Joos
Lieutenant Colonel Philip Eric Bent V. C., D. S. O. (Twice mentioned in Despatches)
9th Bn. Leicestershire Regiment
died 1st October 1917, aged 26.
Panel 50 to 51.
Native of Halifax, Nova Scotia.
Citation:
An extract from "The London Gazette," No. 30471, dated 11th Jan., 1918, records the following:- For most conspicuous bravery, when during a heavy hostile attack, the right of his own command and the battalion on his right were forced back. The situation was critical owing to the confusion caused by the attack and the intense artillery fire. Lt. Col. Bent personally collected a platoon that was in reserve, and together with men from other companies and various regimental details, he organised and led them forward to the counter-attack, after issuing orders to other officers as to the further defence of the line. The counter-attack was successful and the enemy were checked. The coolness and magnificent example shown to all ranks by Lt.-Col. Bent resulted in the securing of a portion of the line which was of essential importance for subsequent operations. This very gallant officer was killed whilst leading a charge which he inspired with the call of "Come on the Tigers."
42537 Corporal William Clamp V. C.
6th Bn. Yorkshire Regiment
died 9th October 1917, aged 26.
Panel Reference Panel 52 to 54 and 162A.,
Son of Charles and Christina Dundas Clamp, of 13C, Reid Terrace, Flemington, Motherwell.
Citation:
An extract from "The London Gazette," No. 30433, dated 18th Dec., 1917, records the following:-"For most conspicuous bravery when an advance was being checked by intense machine-gun fire from concrete blockhouses and by snipers in ruined buildings. Corporal Clamp dashed forward with two men and attempted to rush the largest blockhouse. His first attempt failed owing to the two men with him being knocked out, but he at once collected some bombs, and calling upon two men to follow him, again dashed forward. He was first to reach the blockhouse and hurled in bombs, killing many of the occupants. He then entered and brought out a machine-gun and about twenty prisoners, whom he brought back under heavy fire from neighbouring snipers. This non-commissioned officer then again went forward encouraging and cheering the men, and succeeded in rushing several snipers' posts. He continued to display the greatest heroism until he was killed by a sniper. His magnificent courage and self-sacrifice was of the greatest value and relieved what was undoubtedly a very critical situation.
42364 Lance Corporal Ernest Seaman V. C., M. M.
2nd Bn. Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers
died 29th September 1918, aged 25.
Panel Reference Panel 70 to 72.
Son of Mrs. Sarah Seaman. Born at Norwich, Norfolk.
Citation:
An extract from "The London Gazette," No.31012, dated 15th Nov., 1918, records the following:- "For most conspicuous bravery and devotion to duty. When the right flank of his company was held up by a nest of enemy machine guns, he, with great courage and initiative, rushed forward under heavy fire with his Lewis gun and engaged the position single-handed, capturing two machine guns and twelve prisoners and killing one officer and two men. Later in the day he again rushed another enemy machine-gun position, capturing the gun under heavy fire. He was killed immediately after. His courage and dash were beyond all praise, and it was entirely due to the very gallant conduct of Lce. Cpl. Seaman that his company was enabled to push forward to its objective and capture many prisoners."
Images in this gallery © Werner Van Caneghem
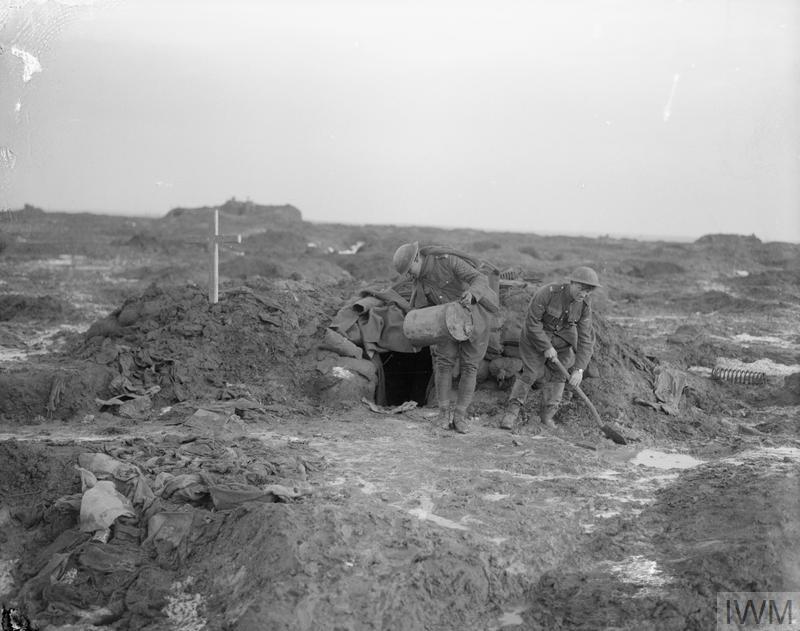

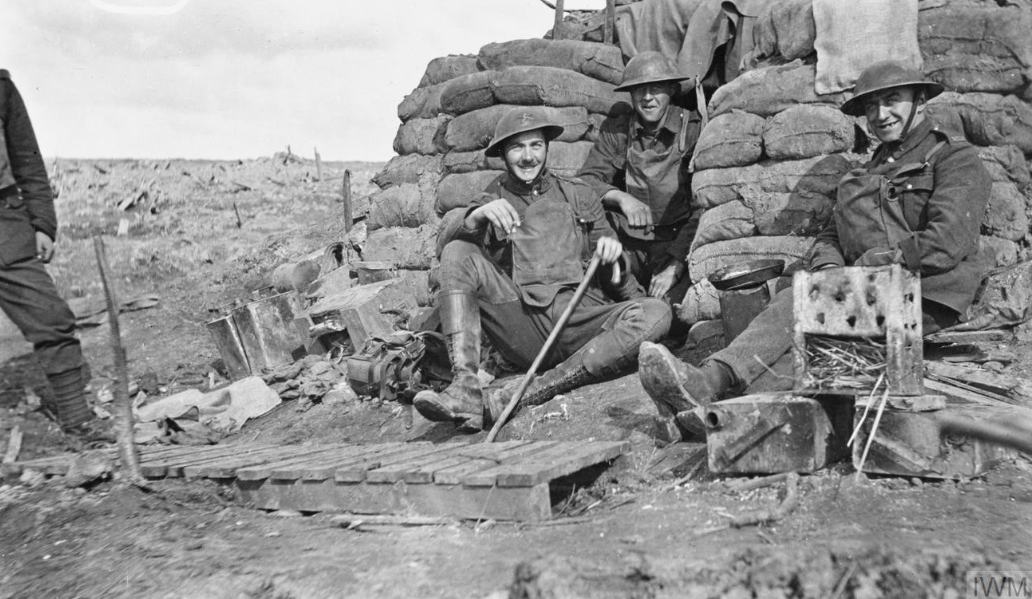
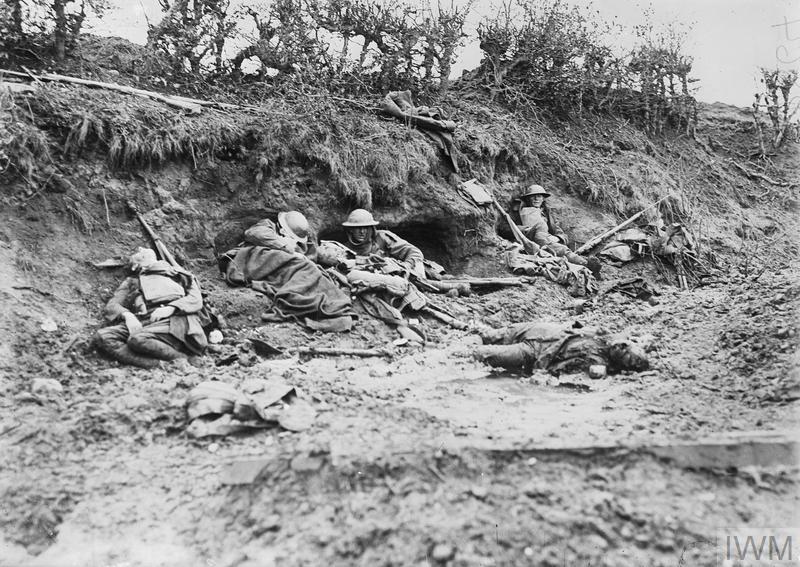
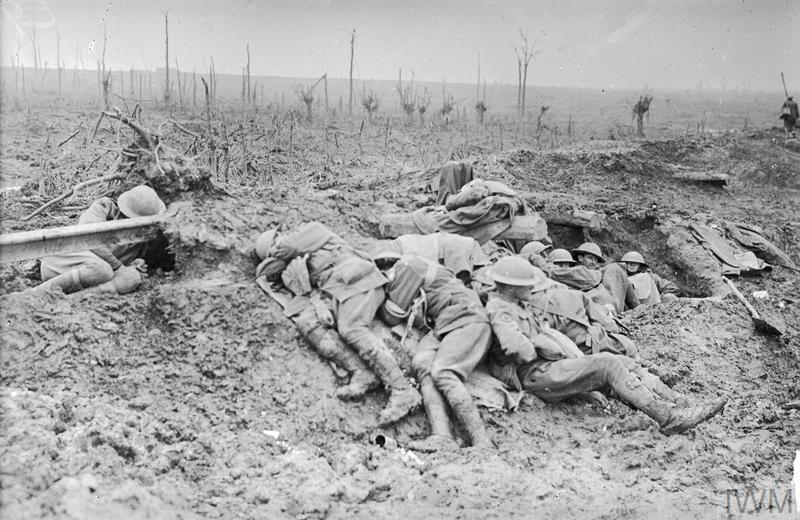
Men from the Royal Garrison Artillery outside their dug-out at Waterloo Farm, near Broodseinde, 11 January 1918. The ground surrounding the dug-out is waterlogged and shell-marked, indications of the heavy fighting and subsequent bad weather in the area. A war grave rests beside the dug-out. © IWM Q 8427